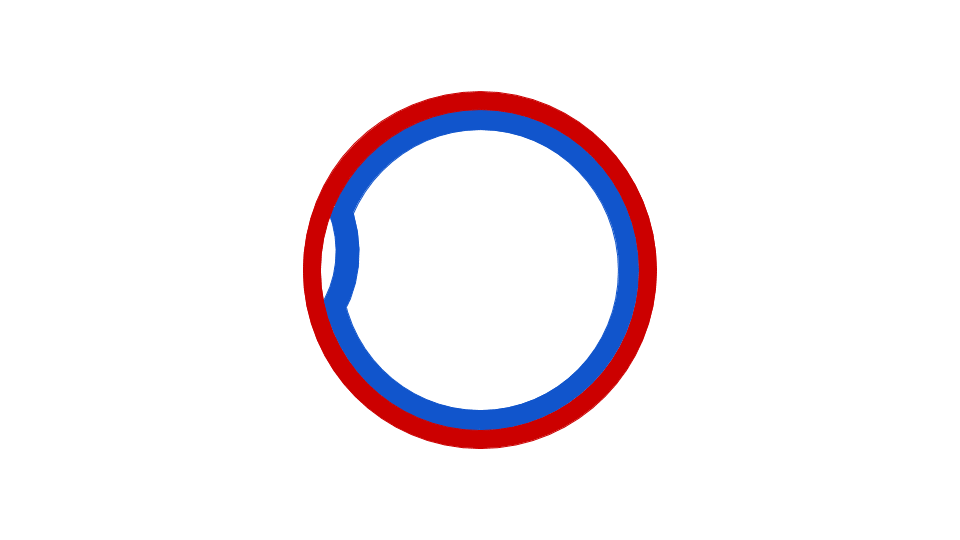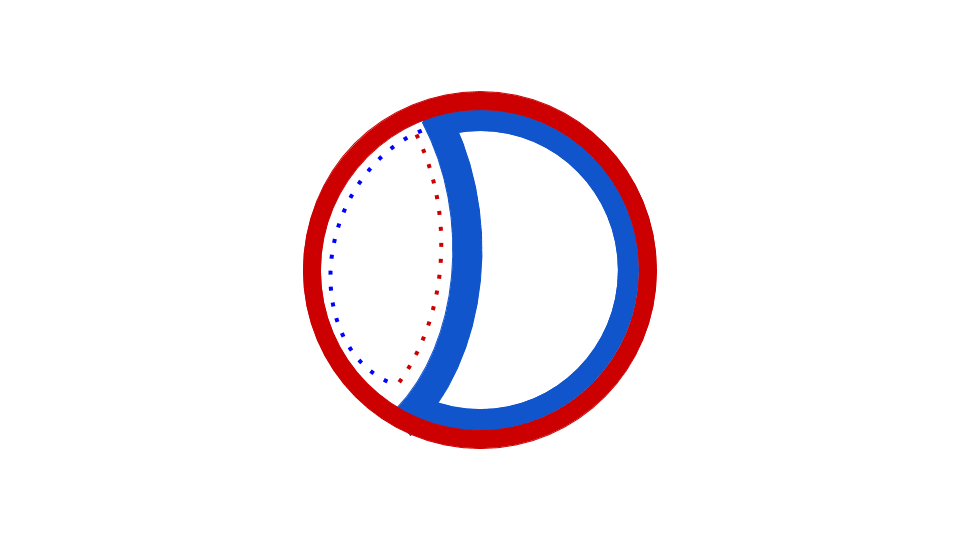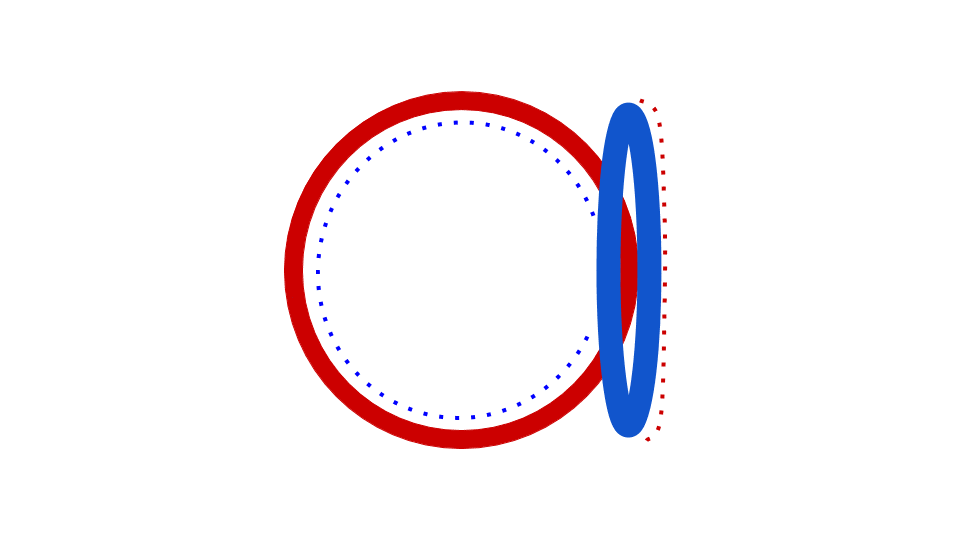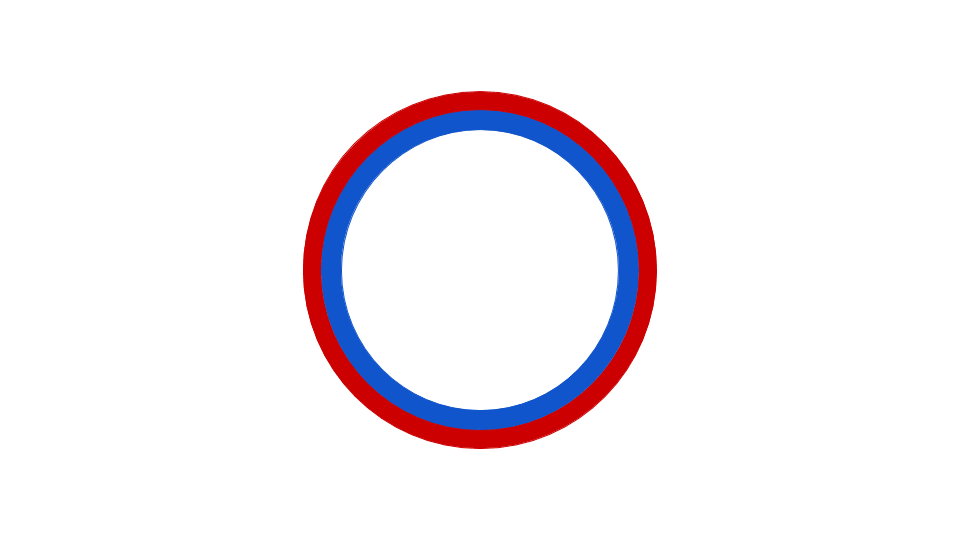
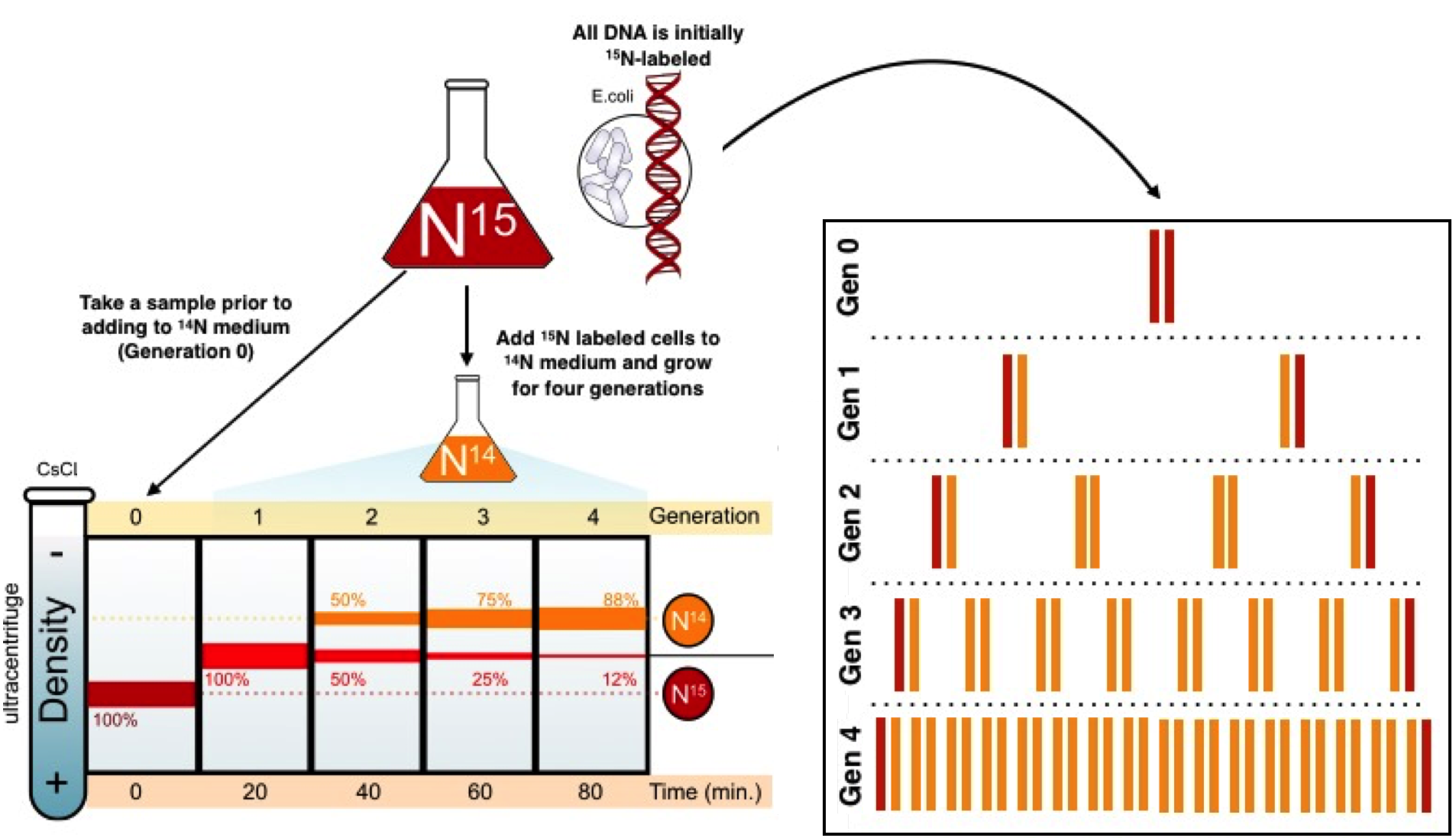
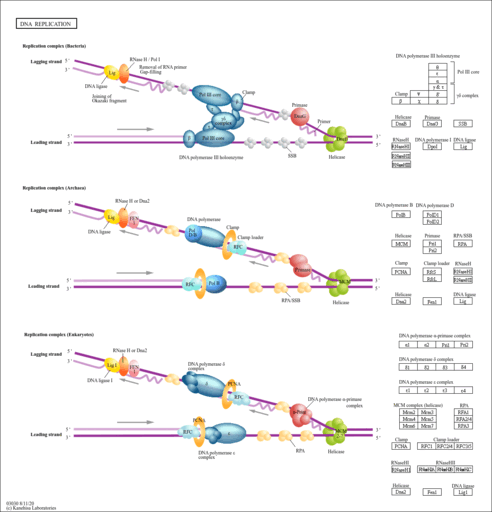
Page 2 The first, known at the time, is that the EColi DNA is a circle The Second point is that DNA is replicated while maintaining the integrity of the circle ie, the circle does not appear to be broken in the process of DNA replication; · DNA replication through the theta mechanism involves melting of the parental strands, synthesis of a primer RNA (pRNA), and initiation of DNA synthesis by covalent extension of the pRNA DNA synthesis is continuous on one of the strands (leading strand) and discontinuous on the other (lagging strand), although synthesis of the two strands seems to be coupled (reviewedThe theta mode is adopted by the prokaryotes to replicate their DNA Their circular DNA has only a single point of origin for replication, unlike the eukaryotic DNA which has multiple origin points to make the process faster The action of helicase enzyme literally unzips the strands of the parental DNA, by breaking the bonds
1
Theta model of dna replication slideshare
Theta model of dna replication slideshare-A) The same DNA polymerase replicates mitochondrial, chloroplast, and nuclear DNA B) There are only two different DNA polymerases that function in the process of replication C) Some DNA polymerases have the ability to function in DNA repair mechanisms D) All eukaryotic DNA polymerases have 3′ → 5′ exonuclease activityThe purpose of DNA replication is to create two daughter DNA molecules which are identical to the parent molecule DNA Replication is SemiConservative Watson and Crick model suggested that DNA replication is semiconservative It implies that half of the DNA is conserved



Replication
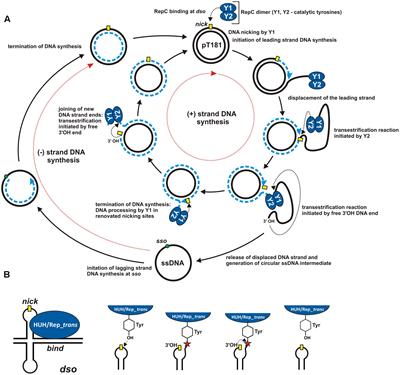
· Polymerase theta (Pol θ, gene name Polq) is a widely conserved DNA polymerase that mediates a microhomologymediated, errorprone, double strand break (DSB) repair pathway, referred to as ThetaBacteriophage lambda genome is one of the classical model replicons in studies on the regulation of DNA replication Moreover, since genes coding for Shiga toxins are located in genomes of lambdoid phages, understanding of mechanisms controlling lambdaIt is a structure formed in replication of circular DNA Since this structure resembles the Greek letter θ it is known as the theta structure Semiconservative mode of DNA replication in bacterial chromosome begins at the origin of replication called ori C, a region of DNA where specific initiation protein gets attached
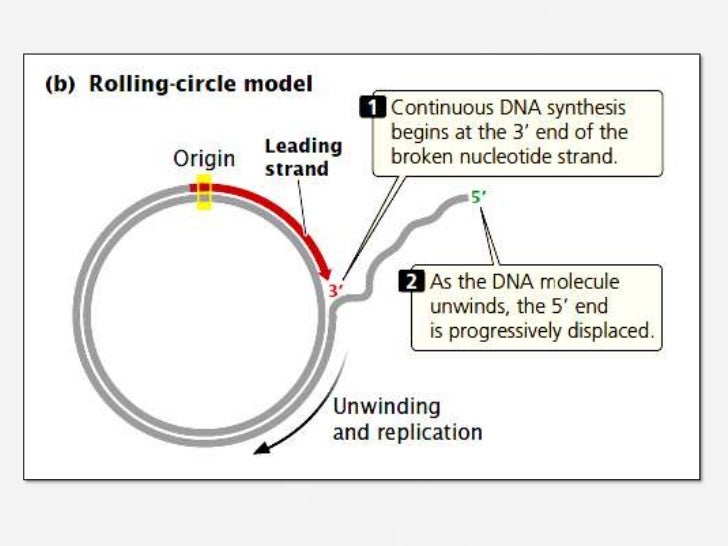
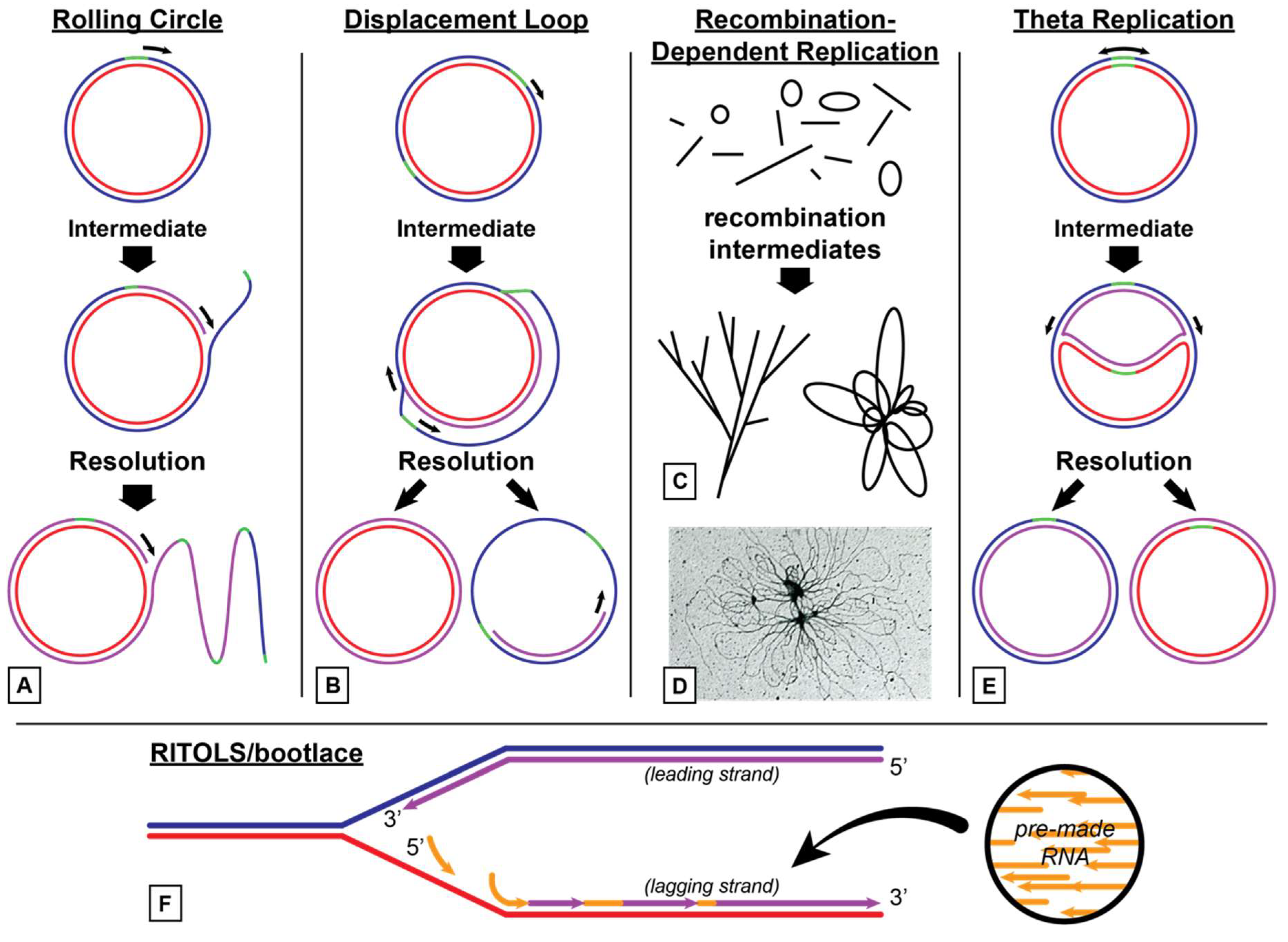
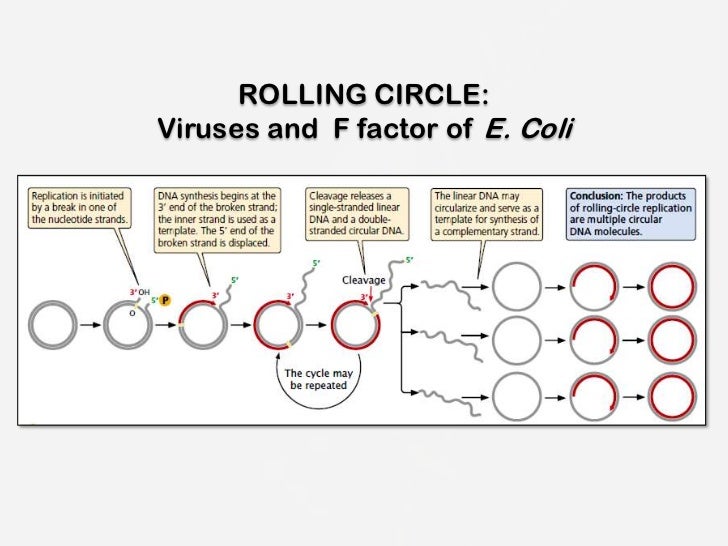
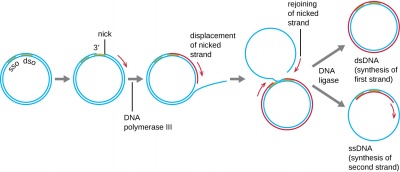
The bacterial chromosome consists of a double stranded DNA ring attached to the plasma membrane Usually there is a single replication fork during replication This is starts at a point called the origin and moves around the chromosome Models Of Replication assignment help, Models Of Replication homework help, dna replication animation, Models Of Replication structure, Models Of Replication · In contrast to the inability to reconstitute the theta model of HSV1 DNA replication, rolling circle replication promoted by extracts of HSV1infected cells has been achieved The first demonstration of rolling circle replication made use of an artificial replication fork consisting of M13 singlestranded DNA to which a complementary oligonucleotide with an unpaired 5′ singleRolling Circle Replication Mechanism in DNA The process of DNA is initiated by initiator protein which nicks at the site called the doublestranded origin on one strand of the doublestrand The initiator protein remains on the 5' phosphate nick strand, and the 3' hydroxyl end of the nicked strand is elongated by DNA polymerase III
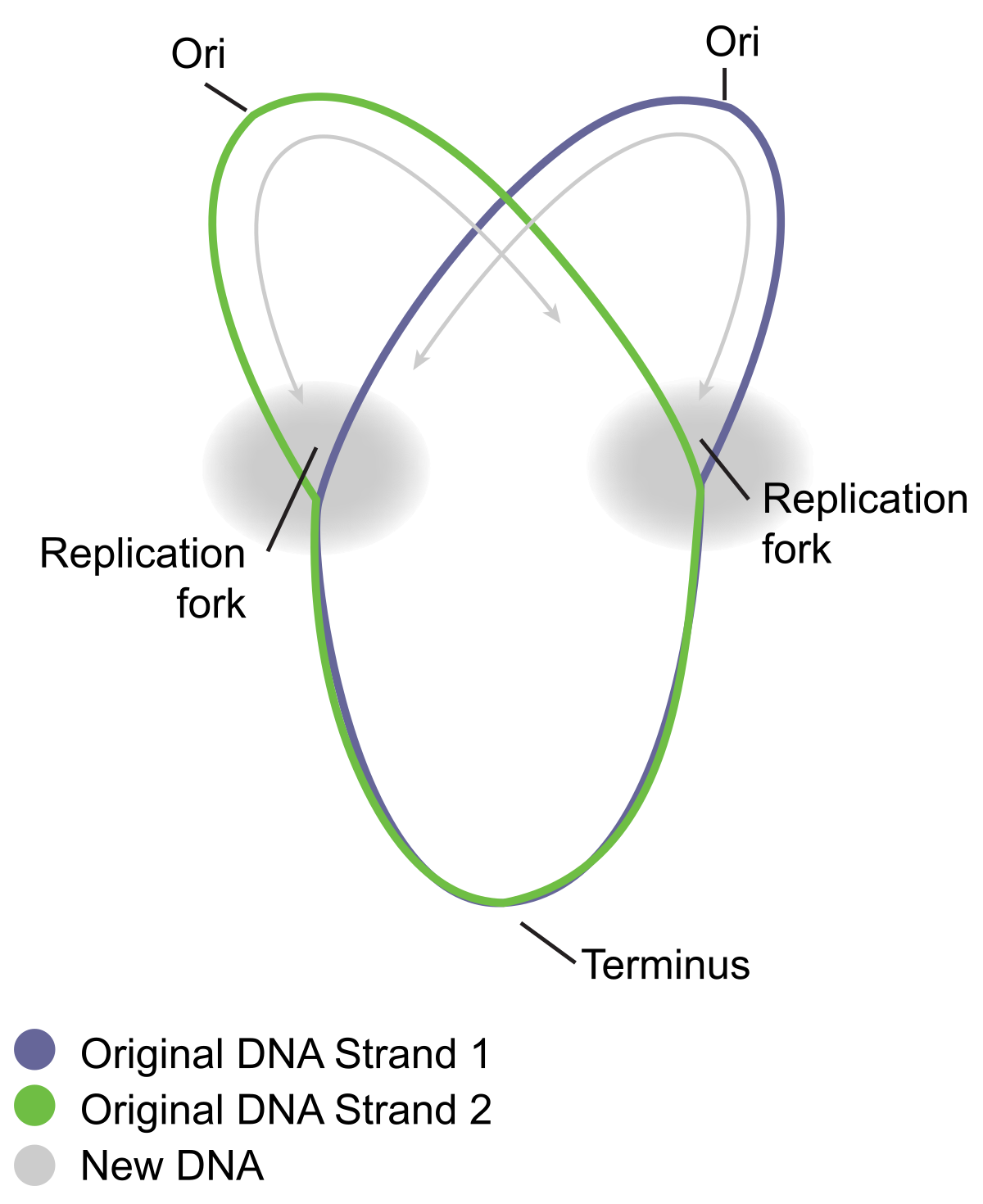
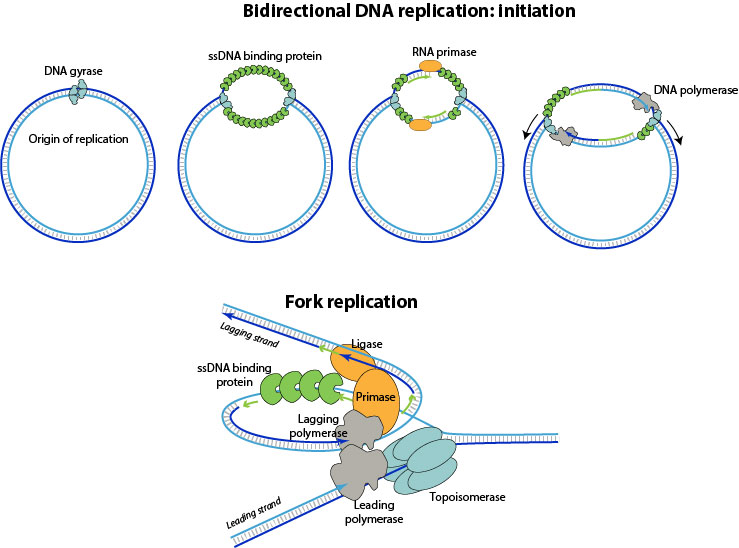
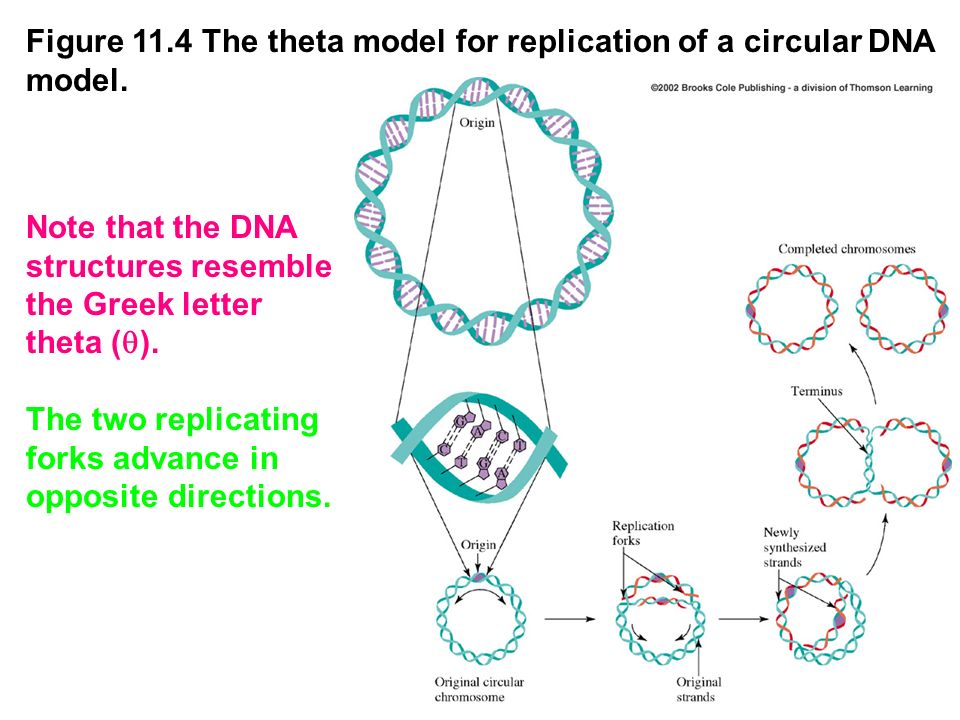
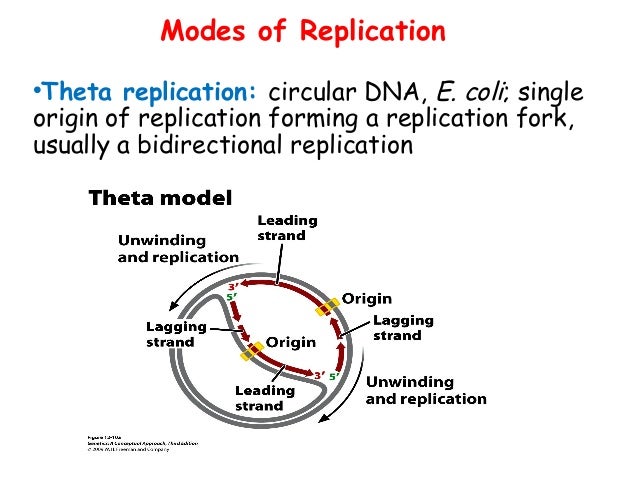
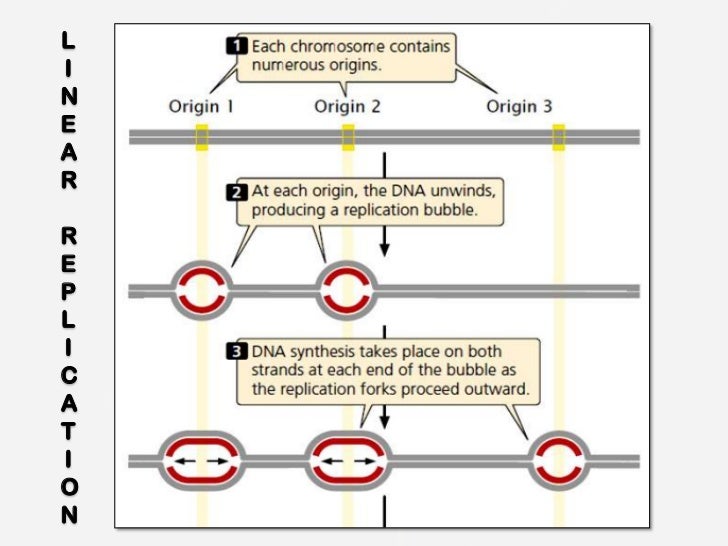
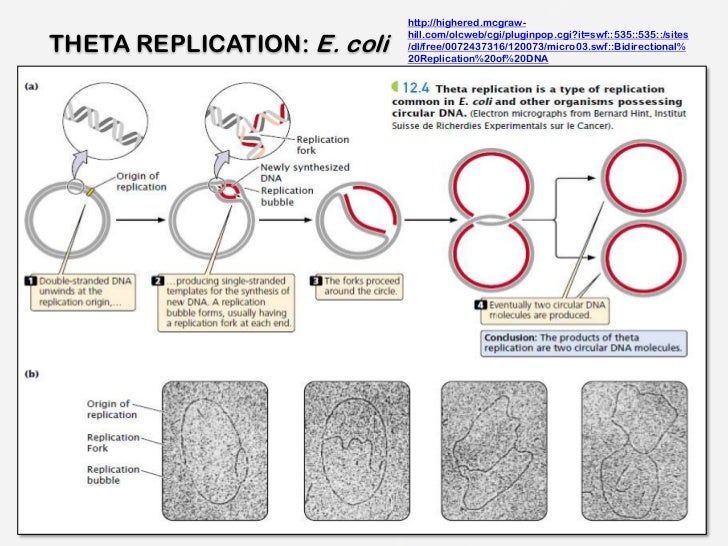
Modes of Replication Theta Rolling circle Linear Theta replication is a type of common inE coliand other organisms possessing circular DNA Doublestranded DNA unwinds at the replication of origin Producing singlestranded templates for the synthesis of new DNAGiovanni Maga, in Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences, 17 The Replicon Model and the Problem of Origins The replicon model, originally formulated by F Jacob in 1963 based on studies on bacterial (Escherichia coli) cells, predicts that replication of a chromosome occurs in discrete units called repliconsEach replicon contains a specific DNA sequence where DNA replication · 1 Initiation As we have seen, DNA synthesis starts at one or more origins or replication These are DNA sequences targeted by initiator proteins in E coli (below) After breaking hydrogen bonds at the origin of replication, the DNA double helix is progressively unzipped in both directions (ie, by bidirectional replication)The separated DNA strands serve as templates for new DNA



Theta Structure Wikipedia



Apps Dso Sws Iastate Edu Si Documentdb Fall 14 Biol Gen 313 Rodermel Br Tuggle Lhhoward Supplementary Pdf
· The replication initiation point (RIP) at the vicinity of an ATrich region in ori1 was identified, and the unidirectional theta replication model of pSCM1 was established To our knowledge, this is the first unidirectional thetatype replication plasmid experimentally identified in the domain of archaeaRolling circle replication or sigma (r) replication a mode of REPLICATION for some doublestranded circular DNA (or RNA) molecules, such as certain BACTERIOPHAGE GENOMESA NICK is first introduced into one of the strands of the doublestranded molecule The other strand remains closed and serves as a TEMPLATE for DNA synthesis The circular structure 'rolls' as synthesisMechanisms of Theta Plasmid Replication Plasmids are autonomously replicating pieces of DNA This article discusses theta plasmid replication, which is a class of circular plasmid replication that includes ColE1like origins of replication popular with expression vectors All modalities of theta plasmid replication initiate synthesis with



Sacbiotech Files Wordpress Com 17 11 The Theta Mode Of Dna Replication In Escherichia Coli Pdf




Replication
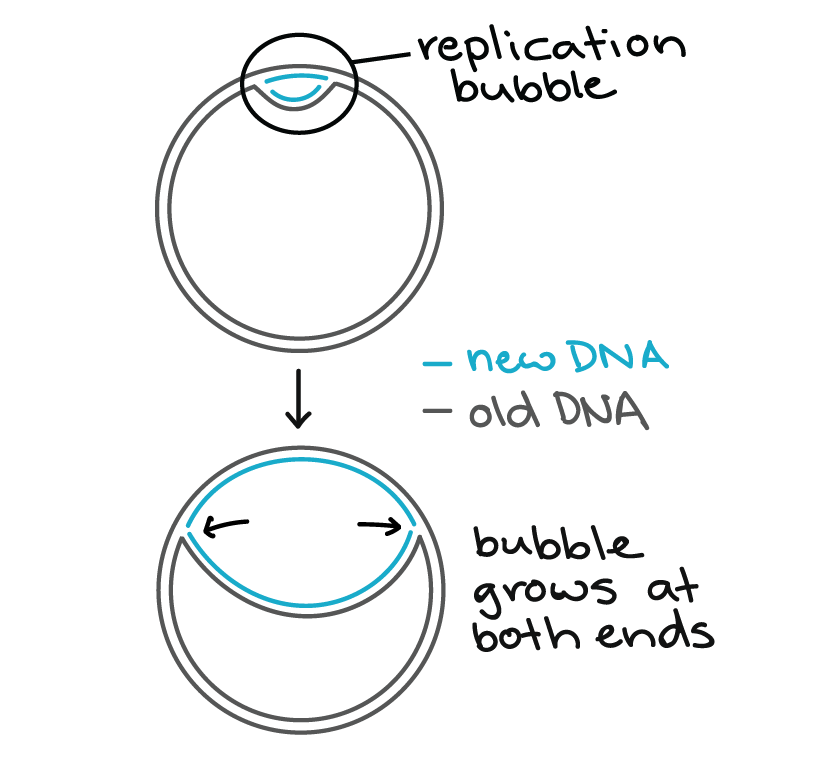
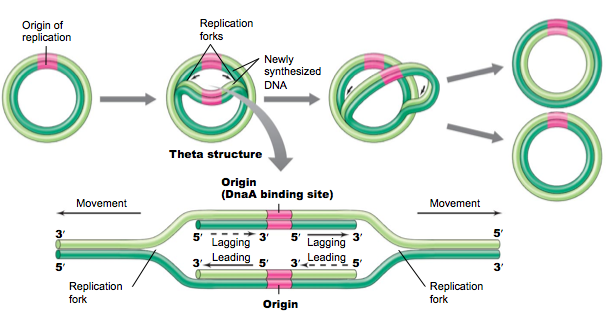
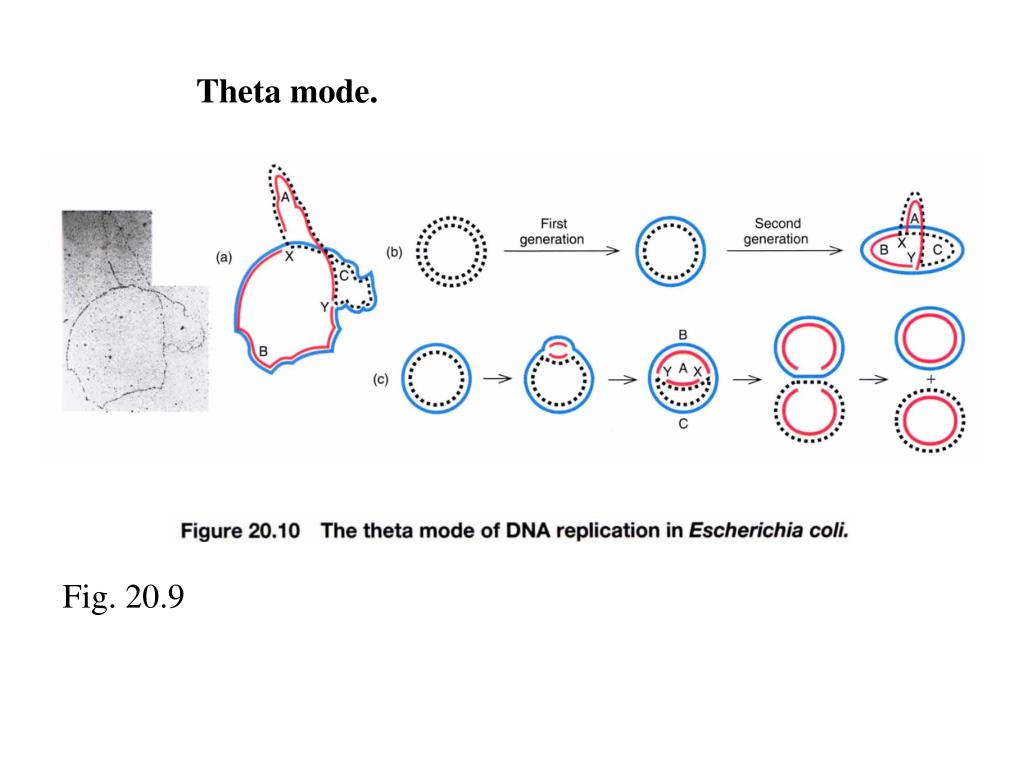
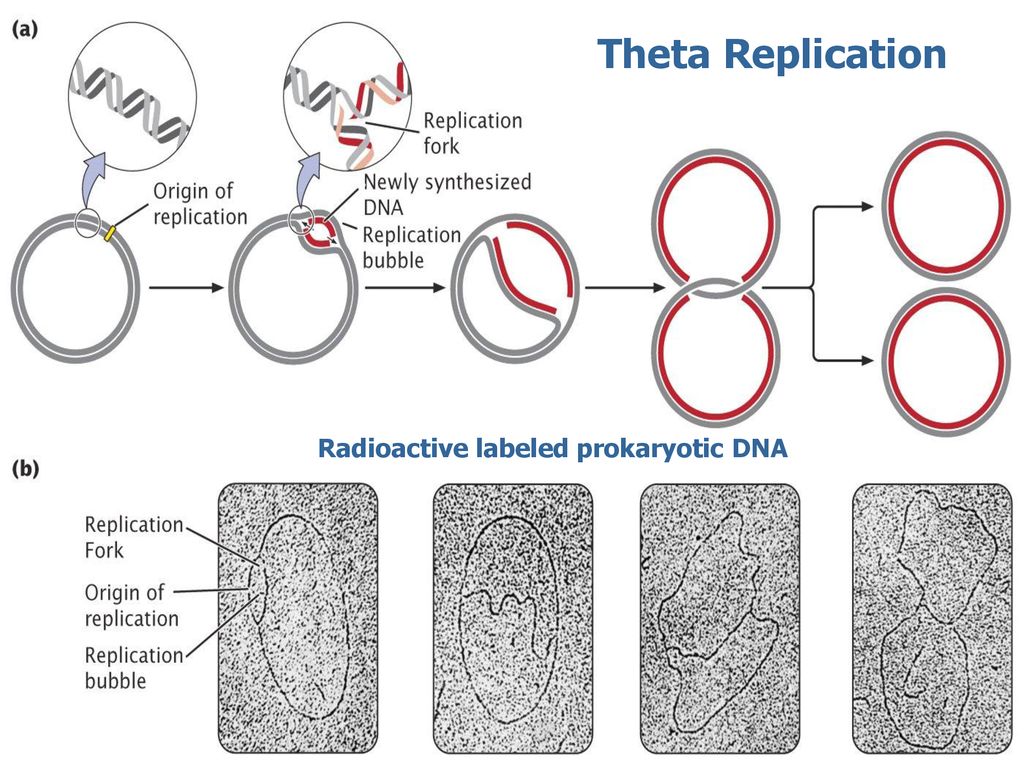
Please answer all questions Draw a molecule of DNA undergoing theta replication On your drawing, identify (a) origin of replication, (b) polarity (5′ and 3′ ends) of all template strands and newly synthesized strands, (c) leading and lagging strands, (d) Okazaki fragments, and (e) locations of · Theta Replication θ is a stage of bidirectional form of replication in a circular DNA molecule (see Fig T44 ) When the two replication forks reach about half way toward the termination sites, the molecule resembles the Greek letter θ DNA replication, θ replication, bidirectional replication, replication, prokaryotes0415 · The theta mode of DNA replication in Escherichia coli (a) An autoradiograph of replicating E coli DNA with an interpretive diagram The DNA was allowed to replicate for one whole generation and part of a second in the presence of radioactive nucleotides to label the DNA



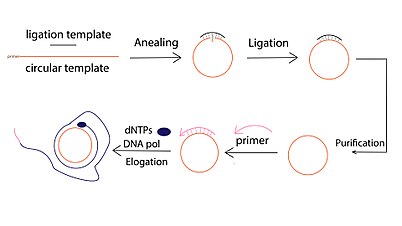
Prokaryotic Dna Replication Wikipedia




Genetics Theta Replication Diagram Quizlet
Rolling circle replication (RCA) is a process of unidirectional nucleic acid replication that can rapidly synthesize multiple copies of circular molecules of DNA or RNA, such as plasmids, the genomes of bacteriophages, and the circular RNA genome of viroids Some eukaryotic viruses also replicate their DNA or RNA via the rolling circle mechanism · Two distinct modes of strand unlinking during thetatype DNA replication Hiasa H (1), Marians KJ (1)Molecular Biology Program, Memorial SloanKettering Cancer Center, New York, New York , USA DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV (Topo IV) are type II bacterial DNA topoisomerases that show a high degree of similarity to each other yet appearTimes Helvetica Symbol Courier class slide template Part Two of BMB 400 Rest of Part Two October 07 class Primase Primers made by DnaG Primosome has many proteins Assay for assembly and migration of the primosome Steps in priming and synthesis Activities of DnaB and PriA in replisome Control of DNA replication Oct 07 Class Replicon = unit that controls replication Thetaform replication



Rolling Circle Replication Wikipedia



Replication Dna
Various models of DNA replication Rolling circle replication θ(theta) mode of replication Replication of linear dsDNA, Replication of the 5'endof linear chromosome Enzymes involved in DNA replication MS SHREYASI DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF BOTANY RAJA NL KHAN WOMENS' COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) GOPE PALACE, MIDNAPURSemiconservative replication for E Coli is initiated by way of a replicon structure which behaves as an autonomous unit of DNA replication This replication element is sometimes called a theta structure, and is circular DNA associated with bacteria and bacteriophages Replication in E Coli starts at origin C, in a region that possess repeatedAn intermediate theta structure is formed which is due to the formation of replication eye
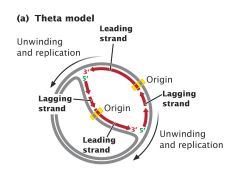



Learn Theta Model Of Replication Meaning Concepts Formulas Through Study Material Notes Embibe Com




Rolling Circle Model Of Dna Replication
· DNA REPLICATION • DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division • In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule This process occurs in all living organisms and is the basis for biological inheritanceDNA replication mechanism is similar in all organisms, the overall method varies depending on the nature of the DNA molecule being replicatedTheta replication, rollingcircle replication, and linear replication differ with respect to the initiatiDNA Replication in Prokaryotes is generally referred to as theta replication#Replication #DNA #Prokaryotes #Theta




Interaction Of The Human Papillomavirus E1 Helicase With Uaf1 Usp1 Promotes Unidirectional Theta Replication Of Viral Genomes Mbio




Biol 3500 Dna Replication Flashcards Quizlet
3003 · Models of DNA Replication To access and download PowerPoint presentation on 'DNA replication' click on the link below Download slides Theta (θ) replication • The bidirectional replication of a circular chromosome in prokaryotes occurs through θ mode of replication0716 · DNA Pol I DNA Pol III Involved in chromosome replication and DNA repair Involved only in chromosome replication Removes primer after DNA synthesis is completed and fills in the gaps Polymerizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides It also has 5' to 3' exonuclease activity apart from 5' to 3' polymerase and 3' to 5 · Plasmid replication Plasmid are replicate autonomously and it also contain origin of replication site There are two models are proposed for plasmid replication 1) Theta θ model 2) Rolling circle model 1) Theta θ model Mostly plasmids in gram negative bacteria replicate in this manners



Dsdna Fork Replication Viralzone




Figure 3 Polyomavirus Jc In The Context Of Immunosuppression A Series Of Adaptive Dna Replication Driven Recombination Events In The Development Of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
DNA Model –Instructions Begin to build your Original DNA strand by gluing the nucleotides together Follow the example Be sure that you always pair AT TA CG The pairs are held GC together by Hydrogen Bonds These are known as the base pairing rules Because of this fact, DNA can replicate exactly, carry genetic information and passThe comprise a large class of animal viruses of considerable public health importance Of the , replication of herpes simplex virus type1 (HSV1) has been the most extensively studied The linear 152kbp HSV1 genome contains three origins of DNA replication and approximately 75 openreading frames Of these frames, seven encode proteins that are required for originspecific DNA replication · DNA replication is bidirectional, and proceeds in a 5'3' direction DNA synthesis takes place simultaneously butin opposite directions on the 2 template strands 12 4 DNA Replication is Semidiscontinuous Replication fork lagging strand Replication fork Leading strand




Engineering Magnetosomes To Express Novel Proteins Which Ones Must Be Suitable For Expressing In Magnetospyrillum Can T Rely On Glycosylation Disulphide Bonds Lipidation Selective Proteol




Chapter 3 Dna Replication 1 Models Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment 2 Dna Synthesis And Elongation 3 Dna Polymerases 4 Origin And Initiation Ppt Download
· Mechanism of Theta Plasmid Replication DNA unwinds at the ori site from where the replication begins It then creates the structure where the whole replicational machinery assembles Since the structure resembles the Greek letter theta (θ), itsDuring DNA replication, theta model of replication E Telomerase uses _____ to synthesize new DNA A) exonuclease activity B) a licensing factor C) strand invasion D) a DNA template E) an RNA template B _____ are tandemly repeated DNA sequences located · Stochastic Model of DNA Replication in the Dark Conceptual and computational details of the model are described in SI Appendix, section VI Briefly, cells of different clock states (θ dark = 0, 2, , 22) were instantiated at the onset of dark (t = 0)




Model For Generation Of Y Form Dnas The Possible Steps Involved In Download Scientific Diagram




Mechanism Of Plasmid Replication Theta And Rolling Circle Dna Replication Online Biology Notes
The theta mode of replication is adapted by the prokaryotes to replicate their genetic material Here, the circular DNA has only a single origin of replication, unlike the eukaryotic DNA which have multiple origins of replication for faster processTheta replication is a type of common in E coli and other organisms possessing circular DNA Doublestranded DNA unwinds at the replication of origin Producing singlestranded templates for the synthesis of new DNA



1




Csir Ugc Net Replication Initiation In Prokaryotes In Hindi Offered By Unacademy



Plos One Analysis Of Replication Intermediates Indicates That Drosophila Melanogaster Mitochondrial Dna Replicates By A Strand Coupled Theta Mechanism




Replicating Animal Mitochondrial Dna




Replication In Circular Dna Theta Model Plantlet




Model For The Role Played By The Vzv Orf29 Protein In Origin Dependent Download Scientific Diagram



1



Bil 250 Lecture 11



Replication



Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy



1




Dna Replication Part 1 Principle Features Figure 11 1 Identical Base Sequences Mechanistic Overview Ppt Download



Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy




Rolling Circle Replication B Sc M Sc Lecture By Ms Pragya Dhakar Youtube




Replication In Circular Dna Theta Model Plantlet




Replication Chapter 7 The Problem Dna Is Maintained In A Compressed Supercoiled State Dna Is Maintained In A Compressed Supercoiled State But Basis Ppt Download



Fch 532 Lecture 11 Chapter 29 Nucleic Acid Structures Ppt Video Online Download




Theta Model And Rolling Circle Model Dna Replication By Bhautik Patel Sir Youtube




Dna Rolling Circle Replication Youtube




Rolling Circle Replication Wikipedia




Theta Model And Rolling Circle Model Of Dna Replication In Prokaryotes Youtube




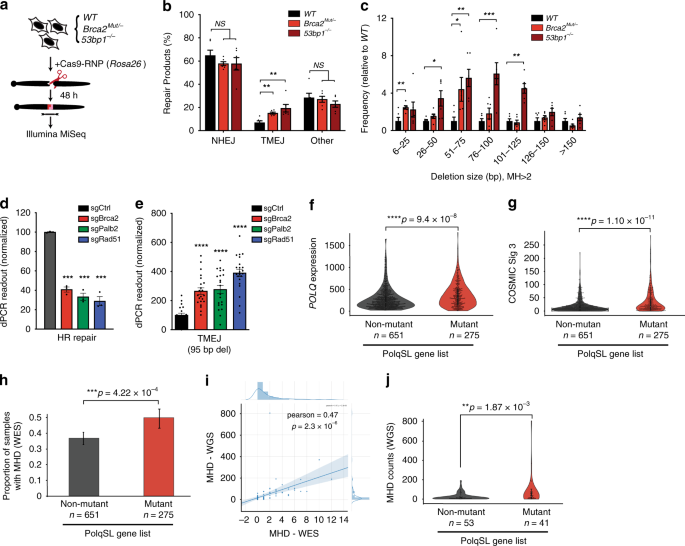
Mutational Signatures Of Non Homologous And Polymerase Theta Mediated End Joining In Embryonic Stem Cells The Embo Journal




Okazaki Fragments Wikipedia




Dna Replication




Iteron An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Quiz 4 Material Up To Oct 22 Flashcards Chegg Com



Sacbiotech Files Wordpress Com 17 11 The Theta Mode Of Dna Replication In Escherichia Coli Pdf



Plants Free Full Text Plant Organelle Genome Replication Html




Figure 3 From Linking Dna Polymerase Theta Structure And Function In Health And Disease Semantic Scholar



P22 Packaging




Mitochondrial Dna Replication And D Loops




Genetics Exam 3 Flashcards Quizlet




Rolling Circle Replication Wikipedia



Replication Class Final Ppt



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1128 Ch3



Ultrasensitive Deletion Detection Links Mitochondrial Dna Replication Disease And Aging Genome Biology Full Text
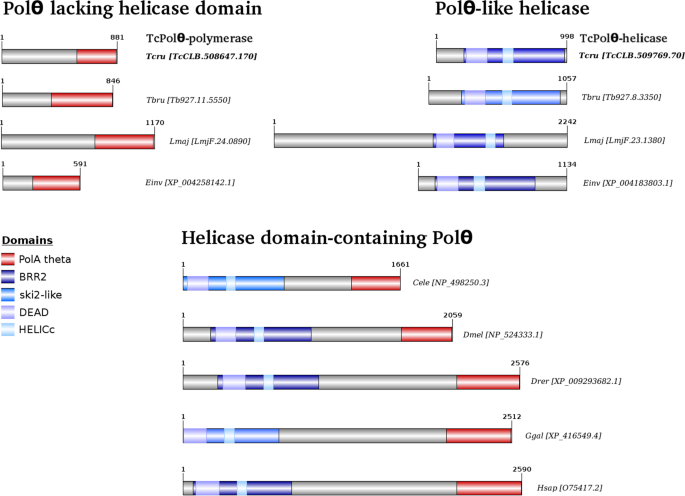



Ortholog Of The Polymerase Theta Helicase Domain Modulates Dna Replication In Trypanosoma Cruzi Scientific Reports



Ppt Dna Metabolism Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Zut Beetgovokm




Chapter 3 Dna Replication Ppt Video Online Download



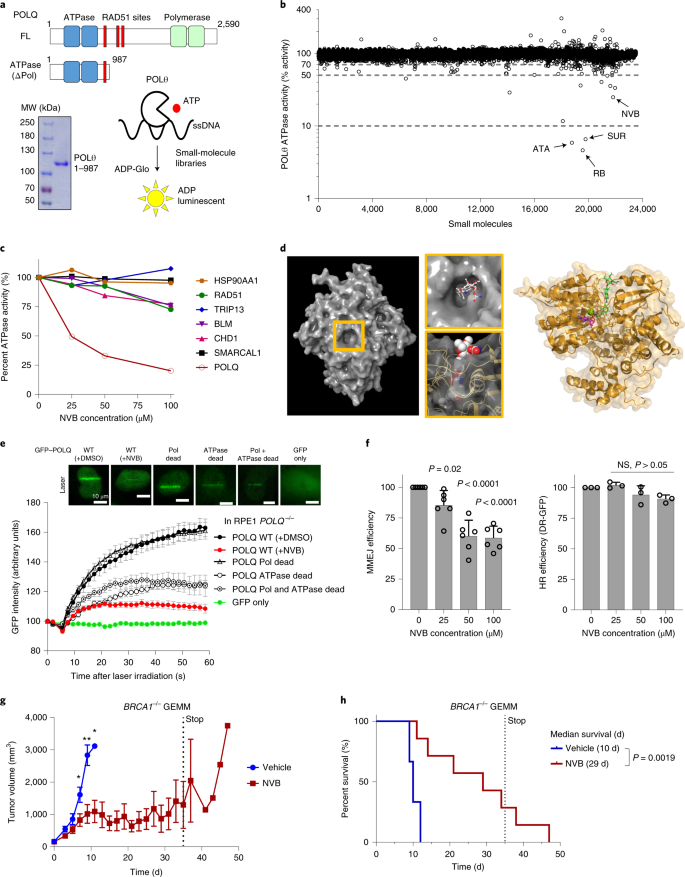
Genetic Determinants Of Cellular Addiction To Dna Polymerase Theta Nature Communications




Pdf Rolling Circle Model Of Replication Magendira Mani Vinayagam Academia Edu



Tmv Ac In Ematerial Zoology Ks Pg sem 2 2 eukaryotic dna replication Pdf



Chapter 12 Topics Models Of Replication Ppt Download




Let S Learn Plants March



Replication




Theta Replication Of Bacterial Dna Download Scientific Diagram




Replication Genetics Britannica



Bil 250 Lecture 11



Http Www Rnlkwc Ac In Pdf Study Material Botany Cc8t Dna Pdf




1 Molecular Genetics 1 Replication And Recombination 2
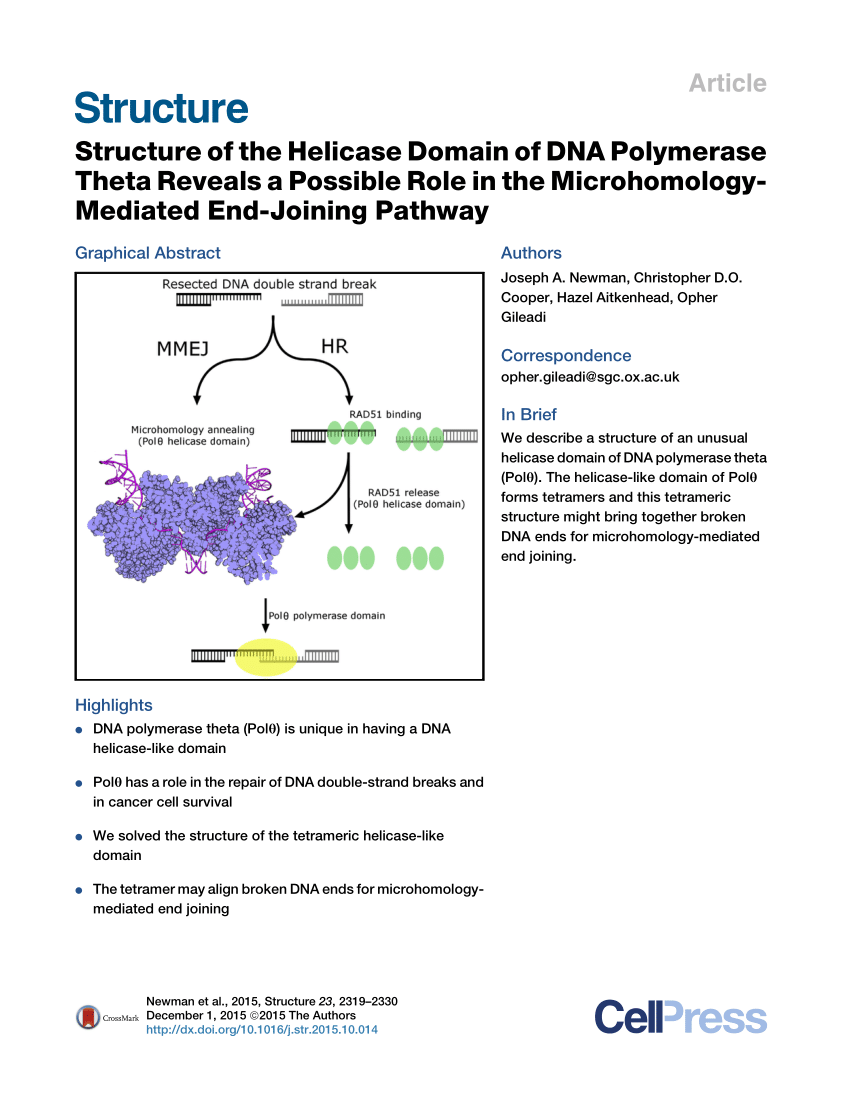



Pdf Structure Of The Helicase Domain Of Dna Polymerase Theta Reveals A Possible Role In The Microhomology Mediated End Joining Pathway



Small Things Considered Pictures Considered 26 Rolling Circle Replication



Sandbox Proteopedia Life In 3d



Replication



Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry




Biology Write Up Biology Articles Assay For Bidirectional Replication Of Dna Prokaryotic Replication Pattern Theta Replication Autoradiograph For Theta Replication Radio Thymidine Experiment Eukaryotic Replication Pattern Pulse Method




Rolling Circle Replication Of An Animal Circovirus Genome In A Theta Replicating Bacterial Plasmid In Escherichia Coli Abstract Europe Pmc




Dna Replication I Theta Model And Rolling Circle Replication Ritu S Biology Hub




Replication In Circular Dna Theta Model Plantlet




Essential Roles For Polymerase 8 Mediated End Joining In The Repair Of Chromosome Breaks Sciencedirect




Theta Replication Of Bacterial Dna Download Scientific Diagram



Rlacollege Edu In Pdf Microbiology Presentations Dna replication models unit 2 lecture 1rkg Pdf



Replication Dna



Frontiers The Different Faces Of Rolling Circle Replication And Its Multifunctional Initiator Proteins Microbiology




Mechanisms Of Dna Replication Termination Semantic Scholar



Mauc Edu Iq Wp Content Uploads Bio lectures 4 D8 D9 84 D8 A8 D8 D9 8a D9 D9 84 D9 D8 Ac D9 8a D8 D9 84 D8 Ac D8 B2 D9 8a D8 A6 D9 854 D9 811 D9 85 D9 85 D8 A8 D8 D8 B1 D9 D8 D9 84 D9 86 D8 B9 D9 8a D9 85 D9 8a Pdf



What Is The Theta Model Of Dna Replication Quora



Http Www Rnlkwc Ac In Pdf Study Material Botany Cc8t Dna Pdf



Http Www Rnlkwc Ac In Pdf Study Material Botany Cc8t Dna Pdf



Kegg Pathway Ko



Sacbiotech Files Wordpress Com 17 11 The Theta Mode Of Dna Replication In Escherichia Coli Pdf




Dna Polymerase 8 Polq Is Important For Repair Of Dna Double Strand Breaks Caused By Fork Collapse Journal Of Biological Chemistry
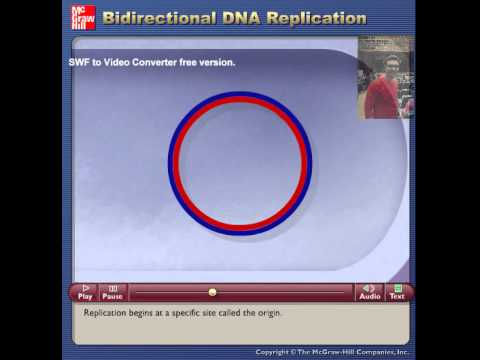



Bidirectional Dna Replication Theta Structure Youtube



Www Jrc Ac In Working Folder Download D 11 53 5f0dbc8 Pdf




Models Of Dna Replication Notes With Definition Diagram Readbiology Com




Rolling Circle Replication An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
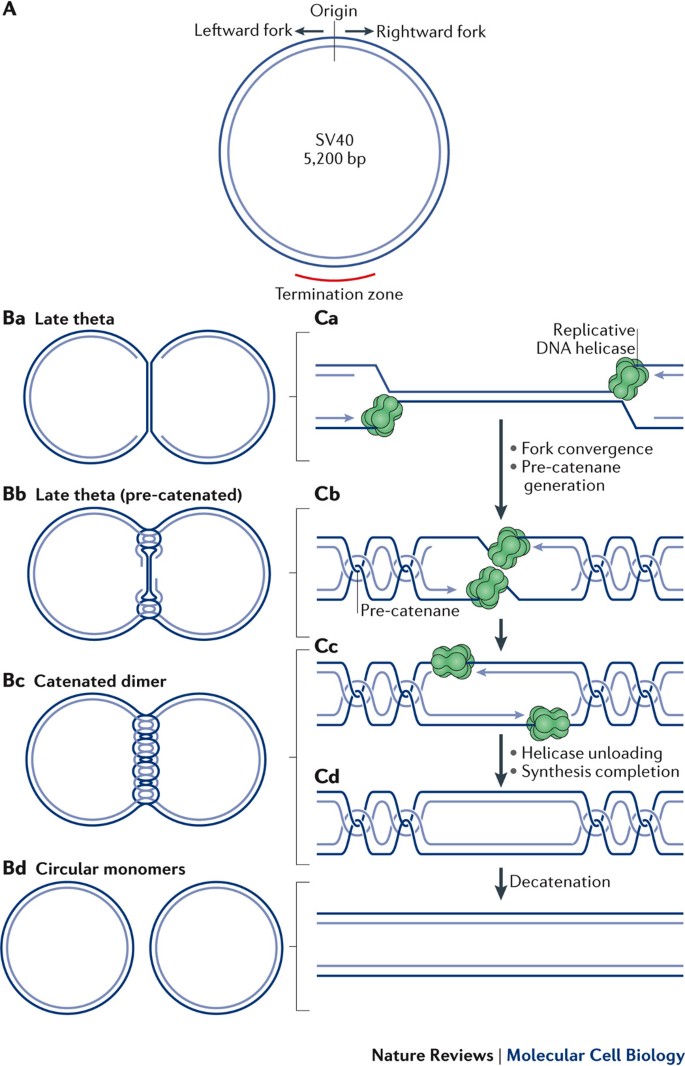



Mechanisms Of Dna Replication Termination Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
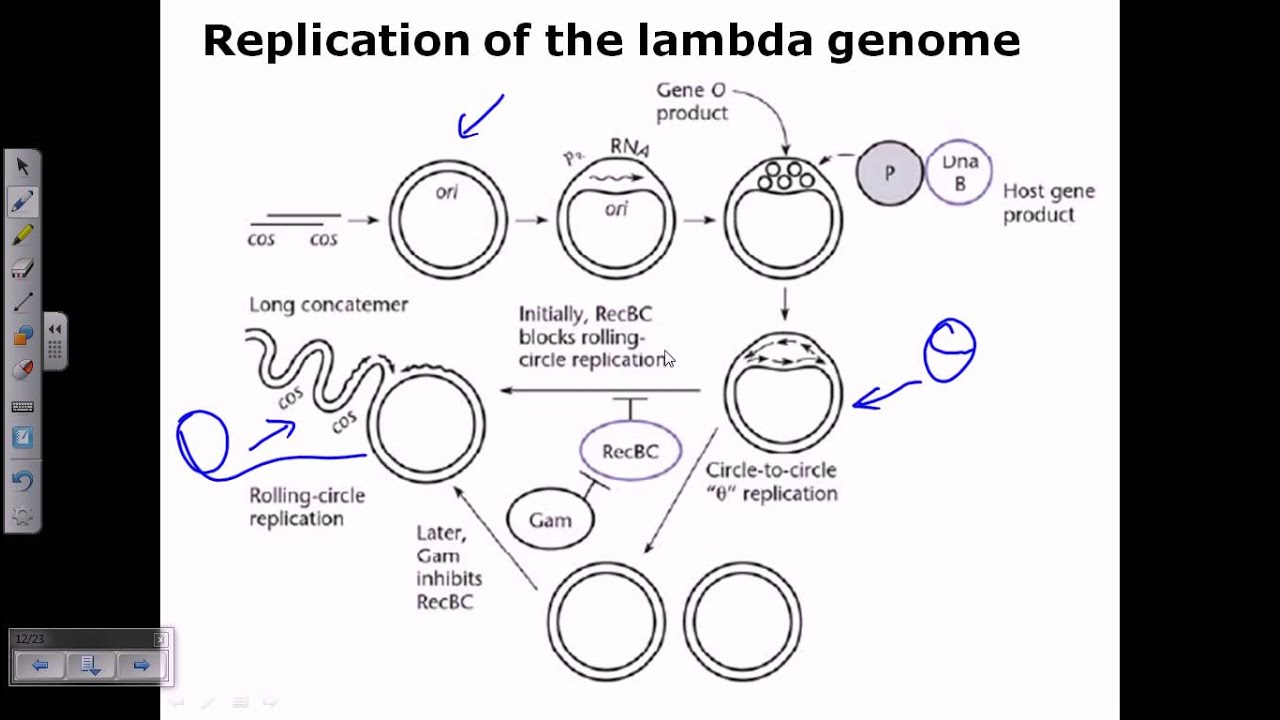



Lambda Phage Genome Replication Youtube
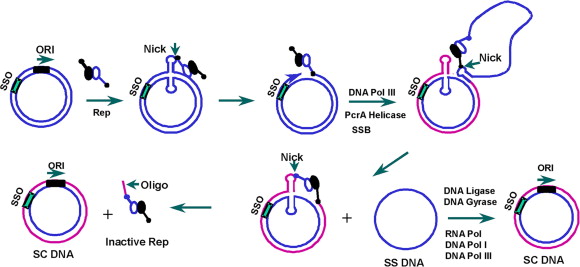



Mechanism Of Plasmid Replication Theta And Rolling Circle Dna Replication Online Biology Notes




Targeting The Dna Repair Enzyme Polymerase 8 In Cancer Therapy Trends In Cancer



Replication



Rlacollege Edu In Pdf Microbiology Presentations Dna replication models unit 2 lecture 1rkg Pdf



Rolling Circle Replication The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki




O Dna Replication Basics Diagram Quizlet



1



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿