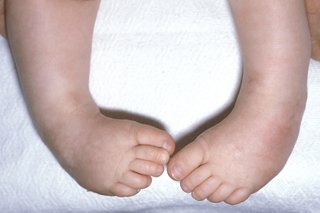
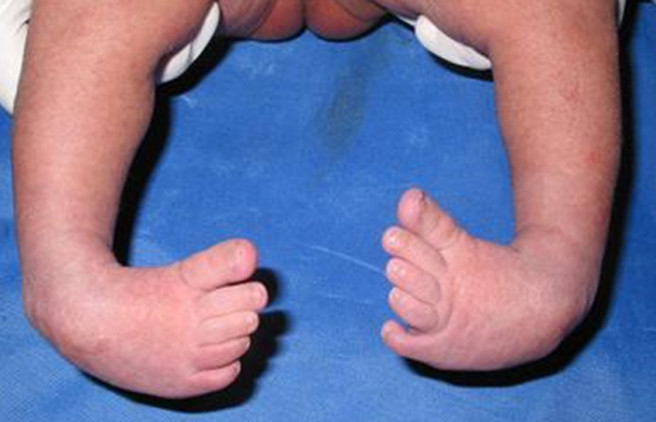
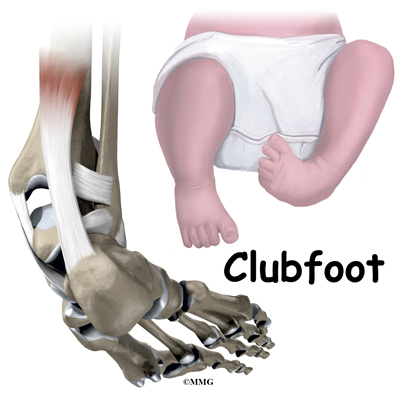
Clubfoot, also known as Congenital Talipes Equinovarus, is a complex, congenital deformity of the foot, that left untreated can limit a person's mobility by making it difficult and painful to walk 1 It is defined as a deformity characterized by complex, malalignment of the foot involving soft and bony structures in the hindfoot, midfoot and forefootClubfoot is a congenital foot deformity that affects a child's bones, muscles, tendons, and blood vessels The front half of an affected foot turns inward and the heel points down In severe cases, the foot is turned so far that the bottom faces sideways or up rather than down The condition, also known as talipes equinovarus, is fairly commonCongenitalclubfoot & Mentalretardation Symptom Checker Possible causes include AlphaMannosidosis Check the full list of possible causes and conditions now!

Club Foot Symptoms And Treatment
Congenital club foot types
Congenital club foot types-Ii 2 Soft > Stiff foot occurs in 33% of cases It is usually a long foot which is more than 50% reducible and treated with casting and attain total correction of feet after 78 month, if not then surgery must required iii Stiff > Soft foot present in 61% of cases It is less than 50% reducible after physiotherapy and casting If specificCongenital club foot (also known as talipes equinovarus) is a pathology in which an infant's foot is turned inward It affects approximately one infant in every 1,000 live births, making it one of the more common congenital foot deformities right after hip dysplasia Congenital clubfoot can affect both feet (bilateral) with a 35 percent chance and it is more frequent in males than in females



Club Foot Nhs
There are two types of clubfoot Isolated or idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type If your child has clubfoot with no other medical problems, it's called isolated clubfoot Idiopathic means that the cause of clubfoot is not known NonisolatedTalk to our Chatbot to narrow down your searchMeSH Terms Achilles Tendon/surgery;
This Classic article is a reprint of the original work by Ignacio V Ponseti and Eugene N Smoley, Congenital Club Foot The Results of Treatment An accompanying biographical sketch on Ignacio V Ponseti, MD, is available at DOI /s and a second Classic article is available at /s 14 Congenital Anomalies Definitions Congenital anomalies comprise a wide range of abnormalities of body structure or function that are present at birth and are of prenatal origin For efficiency and practicality, the focus is commonly on major structural anomalies These are defined as structural changes that have significant medical Congenital talipes equinovarus, also known as 'club foot', is a congenital foot deformity present at birth It is one of the most common congenital deformities The foot consists of 26 bones Most relevant for this congenital deformity are the talus, calcaneus and navicular The calcaneus and navicular are medially rotated in relation to
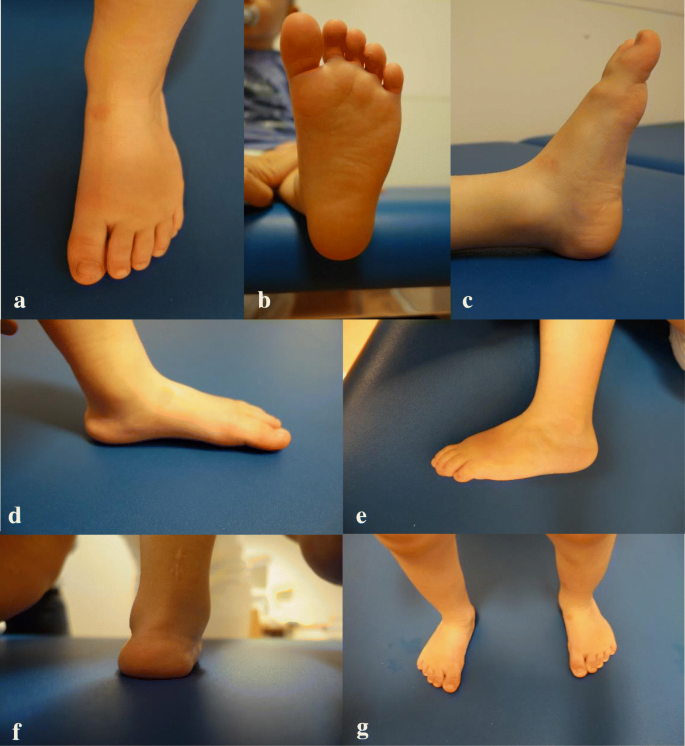
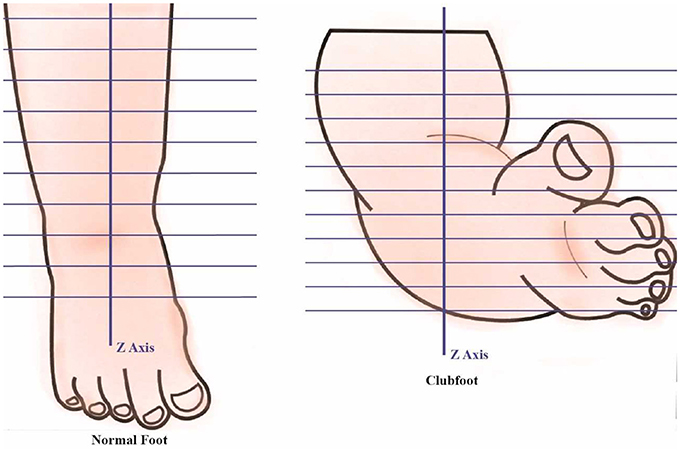
Clubfeet, congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV) Bilateral clubfeet Specialty Orthopedics, podiatry Symptoms Foot that is rotated inwards and downwards Usual onset During early pregnancy Causes Unknown Risk factors Genetics, mother who smokes cigarettes, males Ethnicity Diagnostic method Physical examination, ultrasound during pregnancy INTRODUCTION Talipes Latin talus (ankle) pes (foot) Equino indicates the heel is elevated (like a horse's) varus indicates it is turned inward It is a congenital malformation of the lower extremity that affects the lower leg, ankle, and foot Club foot, also called congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV), is a congenital deformity involving one foot or bothIdiopathic club foot is the most frequent and unless specified otherwise, the term congenital talipes equinovarus represents an idiopathic type In this deformity, the foot is fixed in adduction, supination and varus resulting in inwardly inclined and downward pointing foot



Is Unilateral Lower Leg Orthosis With A Circular Foot Unit In The Treatment Of Idiopathic Clubfeet A Reasonable Bracing Alternative In The Ponseti Method Five Year Results Of A Supraregional Paediatric Orthopaedic Centre




Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot And Other Foot Abnormalities Pediatrics Merck Manuals Professional Edition
Background Congenital idiopathic clubfoot is a very common musculoskeletal birth defect, but with no known etiology Dietz et al have shown possible linkage in chromosome 3 and 13 in a large, multigenerational family with congenital idiopathic clubfoot Current evidence suggests that muscle development is impaired in patients with congenital idiopathic clubfoot, therefore weCauses of Club foot There are three main types of clubfoot Congenital The most common type The cause is unknown, but genetic (inherited) factors may play a role Clubfoot is the only abnormality Positional This type of clubfoot occurs because the foot was in an abnormal position in the womb It is the easiest to treat TeratologicCongenital Talipes Equinovarus is sometimes referred to as club foot Club foot occurs in less than 05% of births It is more common in boys than girls In half of the babies with club foot, both feet are affected The feet need to be corrected;



Ponseti Method For Clubfoot Treatment




4 1 Clubfoot Types Clubfoot Guide 123
Club foot (also called talipes) is where a baby is born with a foot or feet that turn in and under Early treatment should correct it In club foot, 1 foot or both feet point down and inwards with the sole of the foot facing backwards Credit Club foot happens because the Achilles tendon (the large tendon at the back of the ankle) is too shortThe foot may turn in, and in extreme cases, the bottom of the foot can point up Most types of club foot are present at birth (congenital club foot) Club foot can happen in one foot or in both feet In almost half of affected infants, both feet are involved Although club foot is painless in a baby, treatment should begin immediatelySidered that as in club foot of postnatal onset, congenital talipes is due to muscle paralysis or spasm Adams (1873) also inclined towards this categories talipes equinovarus, talipes calcaneovalgus, metatarsus varus, and a fourth class of mixed or other clinical types




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Archives African Journal Of Current Medical Research




Clinical Photographs Showing A The Club Feet Of A 1 5 Month Old Baby Download Scientific Diagram
They won't correct on their own Club foot is a very treatable conditionClub Foot Types / Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia (medicine) a congenital deformity of the foot in which the ankle, heel and toes are twisted Clubfoot can be classified as (1) postural or positional or (2) fixed or rigid Clubfoot is not painful during infancy Most clubfeet can be successfully corrected using the nonsurgical ponseti methodPediatric Clubbed Foot Clubfoot, also known as talipes equinovarus, is a congenital (present at birth) foot deformity It affects the bones, muscles, tendons and blood vessels and can affect one or both feet The foot is usually short and broad in appearance and the heel points downward while the front half of the foot (forefoot) turns inward



Q Tbn And9gcsiqk2gm7zj3ssgnajpf1ujxpqe2efkyujjneftvigthk Bxfrn Usqp Cau



Physical Therapy In Plymouth For Pediatric Issues Clubfoot
With this type of clubfoot, the foot is turned in sharply and the person seems to be walking on their ankle A clubfoot, also known as club foot, congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV), or talipes equinovarus (TEV) is a congenital deformity (present at birth) in which the affected foot appears rotated internally at the ankle the foot points down and inwards and the soles of the CONGENITAL CLUBFOOT Clubfoot is a birth defect where one or both feet are rotated inwards and downwards The affected foot, calf, leg may be smaller than the other In about half of those affected both feet are involved Congenital clubfoot is present at the time of birth and affects the foot or ankle There is no known cause for clubfoot, andKeywords Ponseti's Treatment for Congenital Clubfoot (1963) In 1963, Ignacio Ponseti and Eugene Smoley experimentally determined an effective and minimally invasive method of treating congenital clubfoot Congenital clubfoot is a disorder in which a newborn's foot is rigidly turned inwards and upwards During the early 1960s, orthopedists




What Is Clubfoot Or Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Or Ctev Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Physiotherapy Treatment Of Clubfoot Or Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Or Ctev




Club Foot Nhs
Congenital talipes equinovarus, or club foot, is one of the commonest congenital orthopaedic conditions ged Club Foot, Surgery Club Foot also is known as Giles Smith Syndrome, Congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV), or talipes equinovarus (TEV) The Word " Talipes Equinovarus" comes from Latin Talus (ankle) pes (foot) Equino – indicates the heel is elevated (like a horse's) varus indicates it is turned inward Publication Types English Abstract;
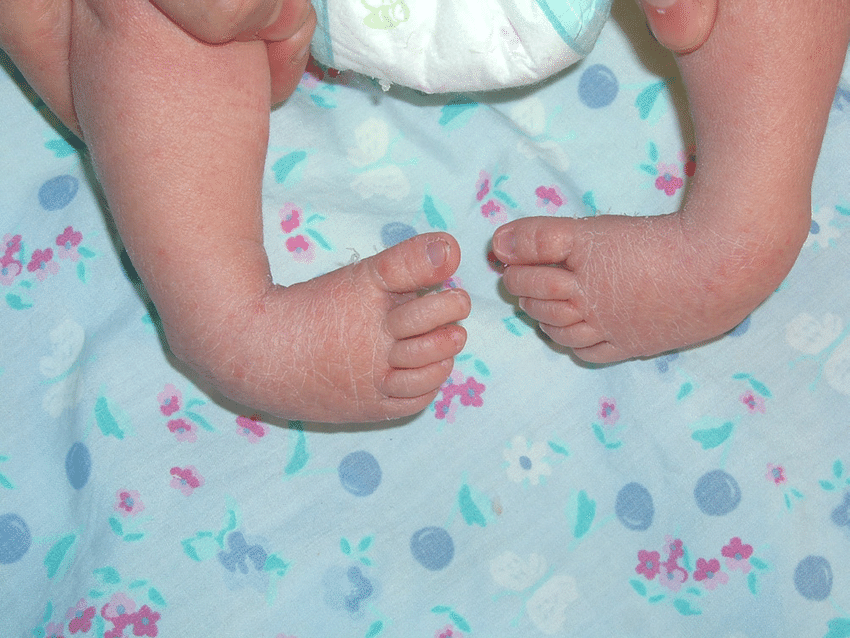



Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot Nursing Care Management Nurseslabs




Talipes Club Foot Health
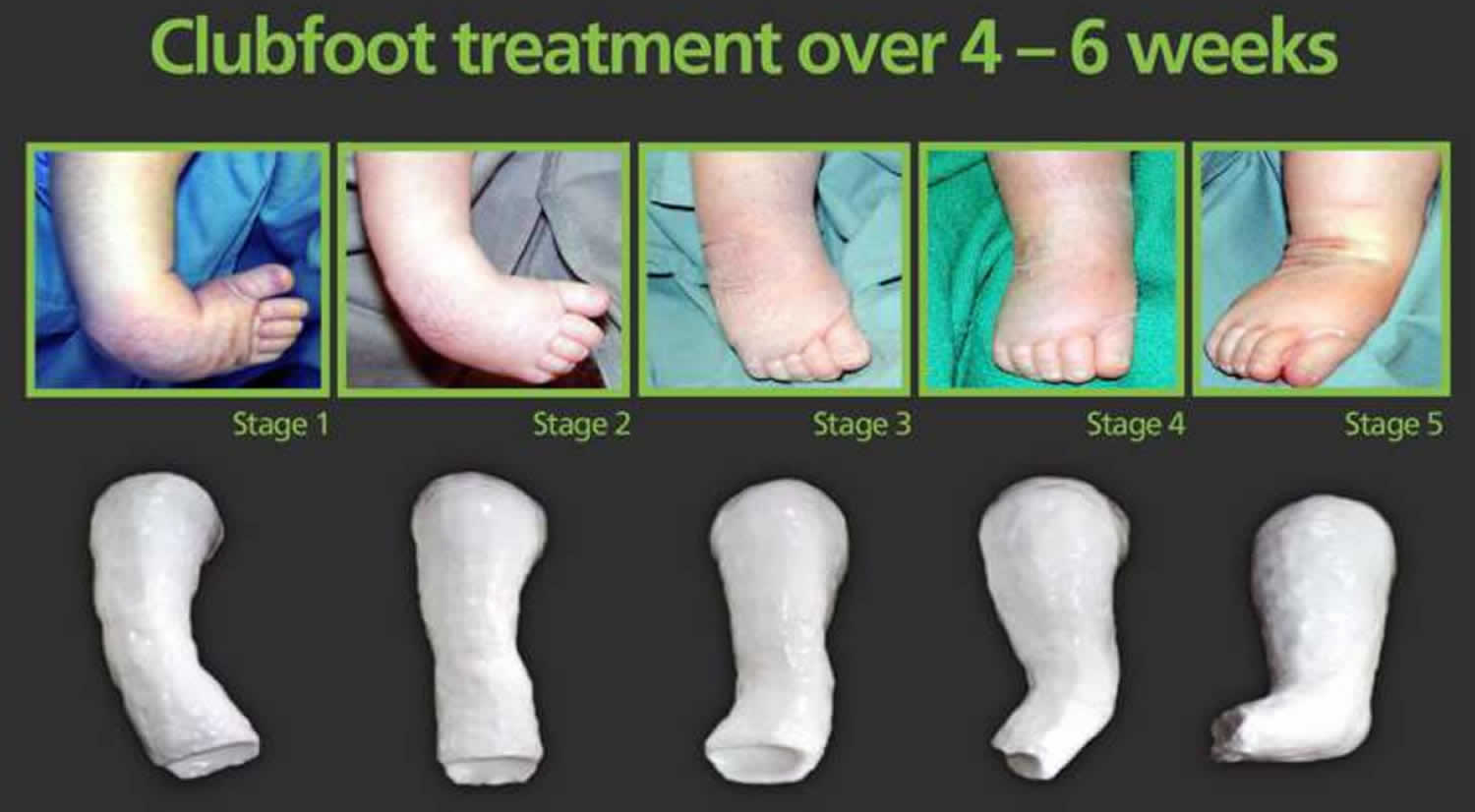
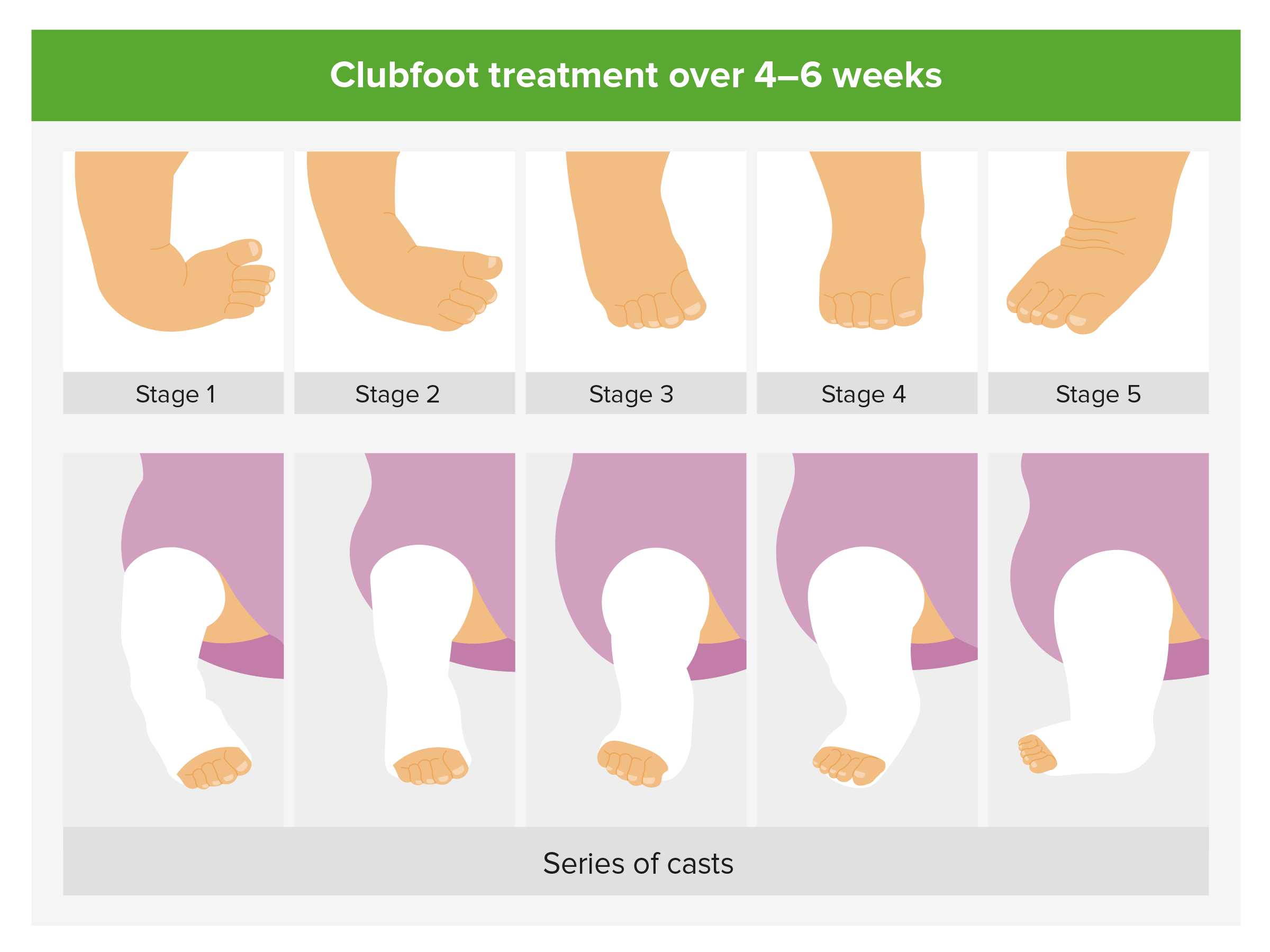
Then, the baby returns to the surgeon about once a week for gentle moving and stretching of the foot, and placement of a new cast Clubfoot won't get better on its own Viewed Trailer To Hell and Back Watch the full trailer of our preseason documentary series To Hell and Back However, the child will walk on the outside border of the foot, or even on the top of the foot PleaseTarsal coalition may be a congenital defect or result from conditions such as injuries or prolonged swelling Treatment of tarsal coalition often includes a cast Sometimes surgically separating the stiffened foot joint restores mobility to the footIn congenital idiopathic clubfoot (ie, talipes equinovarus), the infant's foot points downward (ie, equinus) and turns inward (ie, varus), while the forefoot curls toward the heel (ie, adduction) This congenital disorder has an incidence of 1 in 400 live births, with boys affected twice as



1




Clubfoot Talipes Equinovarus Resurgens Orthopaedics
Clubfoot is a congenital limb deformity defined as fixation of the foot in cavus, adductus, varus, and equinus (ie, inclined inwards, axially rotated outwards, and pointing downwards) with concomitant soft tissue abnormalities (Cardy et al, 07)Congenital clubfoot is a common condition The causes and treatment are still under discussion The author presents the various theories of etiology He believes that the cause is a failure of development of the structures of the foot independent of any extrinsic influences This results inLongterm followup at approximately 30 years showed excellent treatment results, with 'excellent or good' foot function demonstrated in 78% of individuals with clubfoot compared with 85% of matched individuals without congenital foot deformities These outcomes have led to the current situation in most highincome countries where the Ponseti Method is the treatment of choice for




Clubfoot Nurse Key
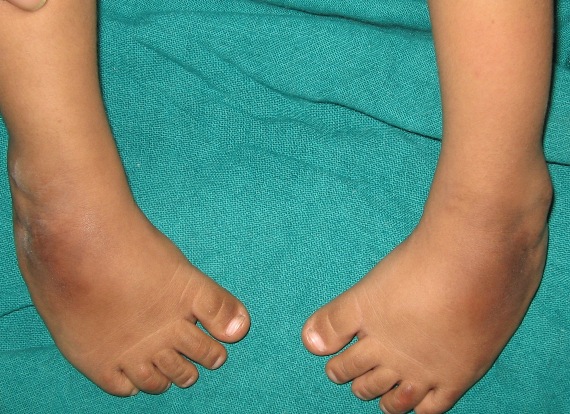



Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Or Club Foot Bone And Spine
The other types of congenital club foot rarely call for operative pro cedures, and yield usually to manipulations, massage and the use of splints when treatment isIdiopathic congenital club foot is probably the most common pediatric orthopaedic problem Despite having been first reported in 1800 However, it's etiology remains unclear The present study proposed a new factor to the ethiopathogenesis of club foot, namely the increased pressure in posterior compartment of the leg during intrauterine CLUB FOOT Types Idiopathic (Unknown Etiology) CongenitalTalipes EquinoVarus CTEV Acquired, Secondary to CNS Disease Spina bifida, Poliomyelitis Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita Absent Bone fibula / tibia
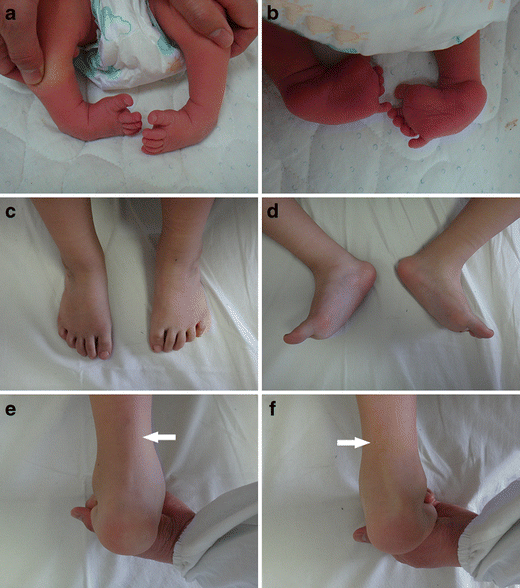



Congenital Clubfoot Early Recognition And Conservative Management For Preventing Late Disabilities Springerlink
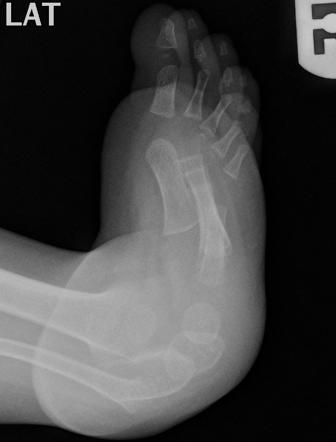



Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets
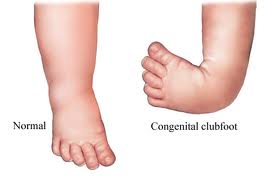
Club foot also known to doctors as congenital talipes equinovarus, is a common birth defect (congenital clubfoot) that can affect one or both feet The child is born with a foot pointing the wrong way – turned down and in – that cannot be placed flat on the ground in the position needed for walking (Figure 1) A longitudinal epiphyseal bracket is rare, occurring in 2–14 % of congenital deformities of the hand and foot Eleven percent of these cases involve the first toe 25 In this entity, the normally transverse epiphysis is Cshaped and oriented along the longitudinal edge of the bone, causing abnormal transverse growth and shortening of the phalanx, as well as angular deformityClubfoot is a foot deformity classified into three different types idiopathic (unknown cause), neurogenic (caused by condition of the nervous system) and syndromic (related to an underlying syndrome) Idiopathic Clubfoot Also known as talipes equinovarus, idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type of clubfoot and is present at birth




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Narayana Health




Clubfoot Phenotype In Pma Pma Mice Human Newborn With Congenital Download Scientific Diagram
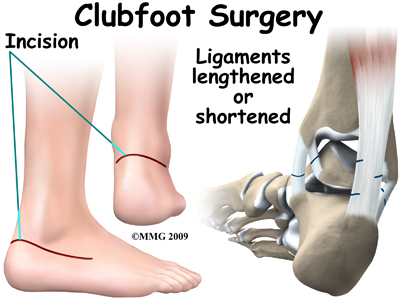
Congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV), also known as clubfoot, is a common congenital orthopaedic condition characterised by an excessively turnedin foot (equinovarus) and high medial longitudinal arch (cavus) If left untreated it can result in longterm disability, deformity and pain Interventions can be conservative (such as splinting orClub Foot Types Clubfoot Deformity Clubfoot can be classified as (1) postural or positional or (2) fixed or rigid Club foot can affect 1 or both feet In clubfoot, the tendons on the inside of the leg are shortened, the bones have an unusual shape, and the achilles tendon is tightenedWe operated on 111 patients with 159 congenital club feet with the aim of correcting the deformity and achieving dynamic muscle balance Clinical and biomechanical assessment was undertaken at least six years after operation when the patient was more than 13 years of age The mean followup was for 11 years 10 months (6 to 36 years)




Clubfoot Wikipedia



2 Congenital Talipes Flip Ebook Pages 1 50 Anyflip Anyflip
Club Foot Types / Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia / It is a congenital malformation of the lower extremity that affects the lower leg, ankle, and foot Club foot, also called congenital talipes equinovarus (ctev), is Idiopathic (unknown cause), neurogenic (caused by condition of the nervous system) and syndromic (related to an underlying syndrome) Clubfoot, also known as congenital talipes equinovarus, is a common idiopathic deformity of the foot that presents in neonates Diagnosis is made clinically with a resting equinovarus deformity of the foot Treatment is usually ponseti method casting




Clubfoot Wikipedia



Clubfoot In Babies And Children




Clubfoot Repair Treatments Procedure Outlook



Clubfoot Eorthopod Com



Foot Deformities Concise Medical Knowledge




Pdf Current Conservative Management And Classification Of Club Foot A Review Semantic Scholar




Foot Deformities Various Talipes Conditions Pediatric Physical Therapy Pediatric Nursing Medical Terms




Idiopathic Talipes Equinovarus Congenital Clubfoot Disclaimer The Findings




What Is Clubfoot Symptoms And Treatment Familydoctor Org




Clubfoot Closeup Of A Newborn Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock



Frontiers Developing A Three Dimensional 3d Assessment Method For Clubfoot A Study Protocol Physiology
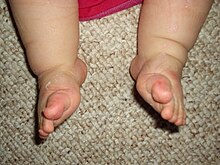



Clubfoot Wikipedia




Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital
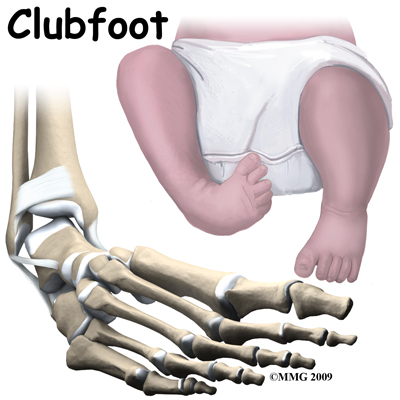



Physical Therapy In Colorado Springs For Pediatric Issues Clubfoot




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets
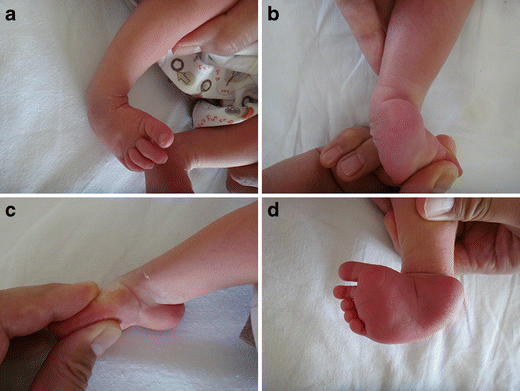



Congenital Clubfoot Early Recognition And Conservative Management For Preventing Late Disabilities Springerlink
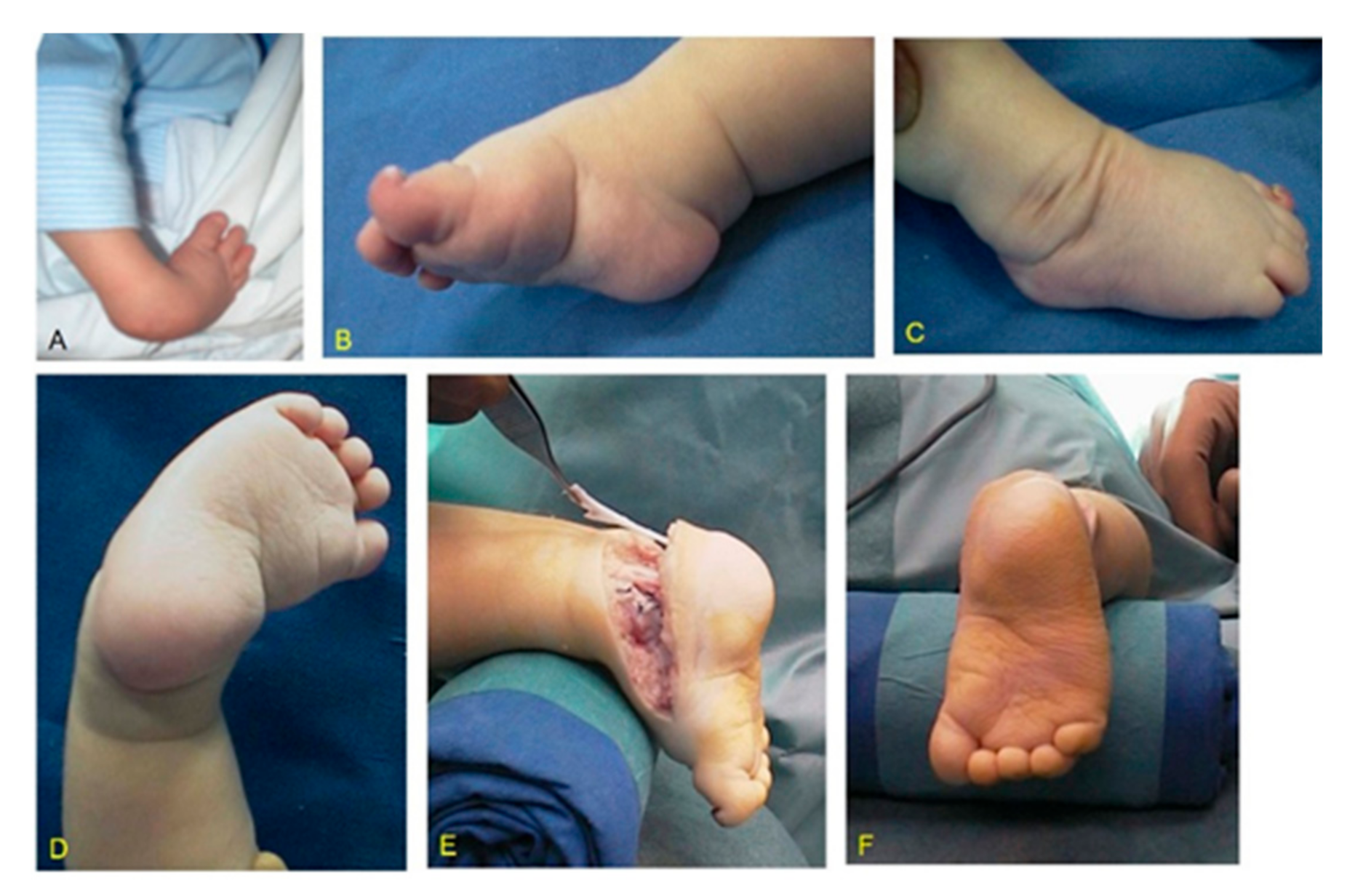



Children Free Full Text Surgical Treatment Of Clubfoot In Children With Moebius Syndrome Html




Scielo Brasil Pe Torto Congenito Pe Torto Congenito



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets




Challenging Clubfeet The Arthrogrypotic Clubfoot And The Complex Clubfoot Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics




Clubfoot Orthopaedia




Congenital Clubfoot Genetic Disorders Types Of Clubfoot




Clubfoot Eorthopod Com



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os




The Newborn Foot American Family Physician



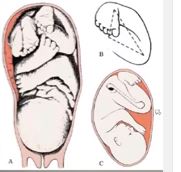
Clubfoot Congenital Equinovarus Cev Team Bone
/clubfoot_baby-56a6fb5d5f9b58b7d0e5d472.jpg)



Photos Of Babies With A Clubfoot




Treatment Of Relapsed Residual And Neglected Clubfoot Adjunctive Surgery Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics




Club Foot Pdf Foot Congenital Disorder



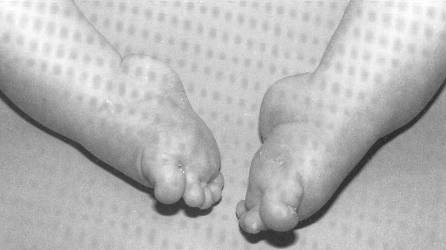
Club Foot Faqs




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Or Club Foot Bone And Spine
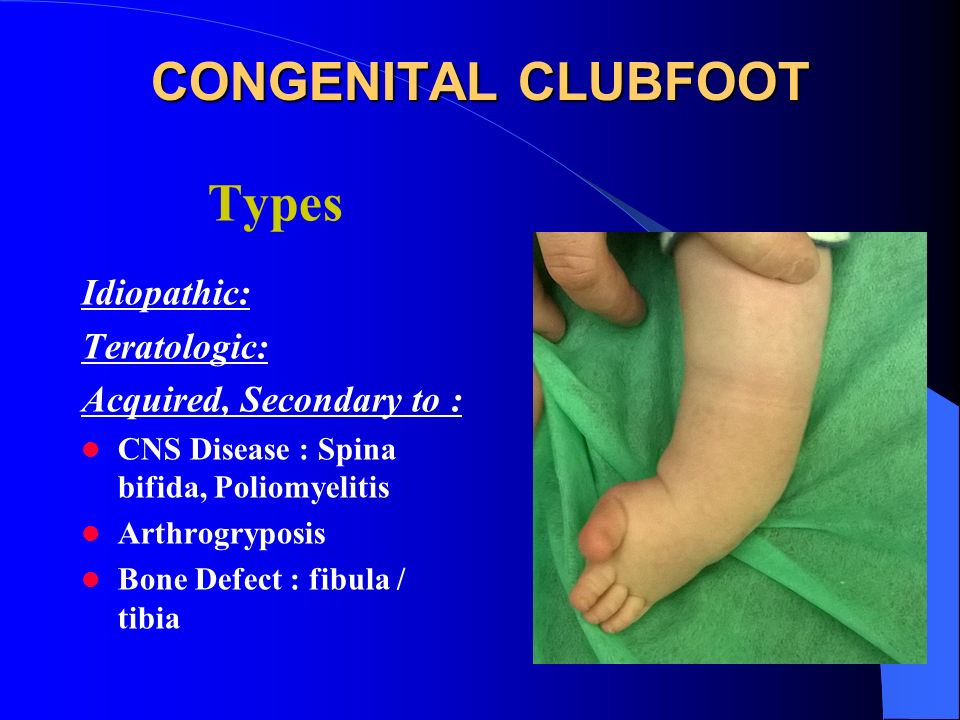



Congenital Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Ppt Video Online Download




Club Foot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus The Nepali Doctor




Club Foot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus About Club Foot Patient
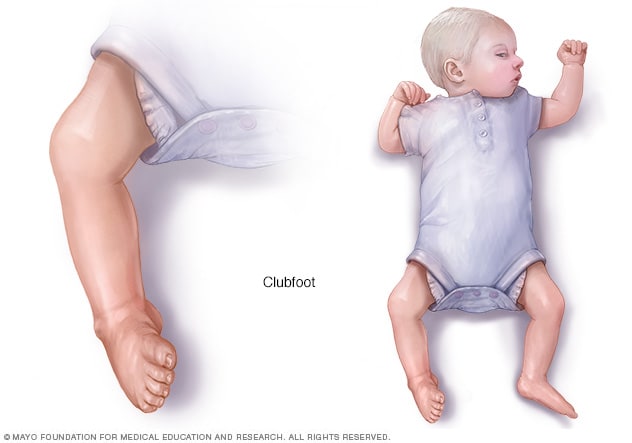



Clubfoot Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic




Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Merck Manuals Consumer Version
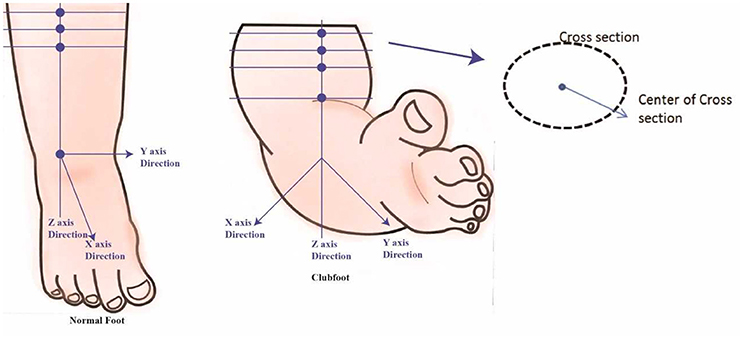



Frontiers Developing A Three Dimensional 3d Assessment Method For Clubfoot A Study Protocol Physiology




Clubfoot Flip Ebook Pages 1 Anyflip Anyflip



1



Congenital Clubfoot Youtube




Pdf Current Conservative Management And Classification Of Club Foot A Review Semantic Scholar
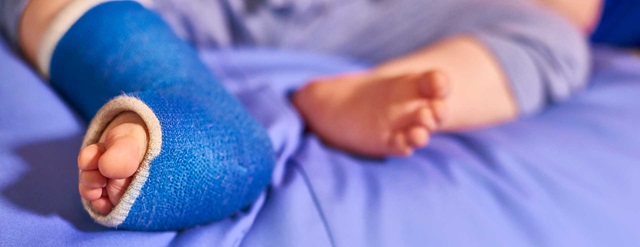



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine




By Cassie Maier What Is Club Foot Club Foot Is When One Or Both Babies Feet Are Turned Inward And Downward And Cannot Be Put Into Normal Position Easily Ppt Download




Club Foot Symptoms And Treatment



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments




Clubfoot Foot And Ankle Deformities Principles And Management Of Pediatric Foot And Ankle Deformities And Malformations 1 Ed




Common Childhood Foot Deformities Consultant360




Clubfoot Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Clubfoot
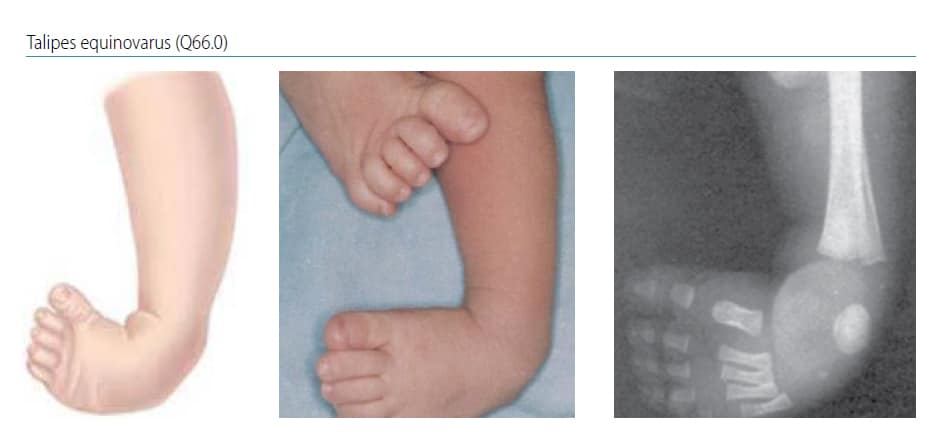



Chapter 4 9 Talipes Equinovarus Talipes Equinovarus Q66 0 Cdc




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Narayana Health




Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital




Nursing Care Plan Clubfoot Or Talipes Equinovarus Nursing Crib



Clubfoot Symptoms Stages Definition Description Demographics Causes And Symptoms Diagnosis




Club Foot Pdf Foot Congenital Disorder



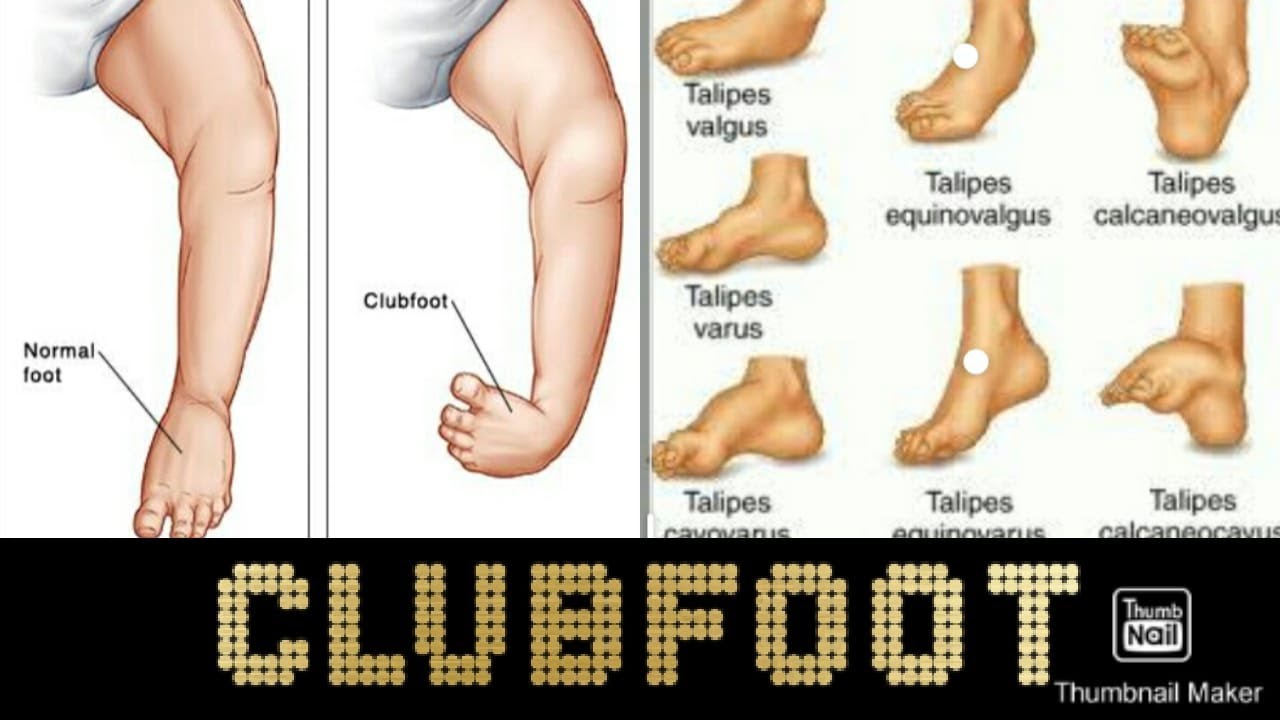
Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot Nursing Care Management Pediatric Physical Therapy Medical Anatomy Medical



Clubfoot Its Types And Causes Simplified In Hindi Youtube



Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot Orthopaedicprinciples Com



Club Foot Talipes Equinovarus Ankle Foot And Orthotic Centre




Club Foot



2



Before Going To Doctor Which Must Know About Clubfoot Rxharun




Current Concepts With The Ponseti Technique




Club Foot Talipes In Babies Causes Signs Treatment Youtube
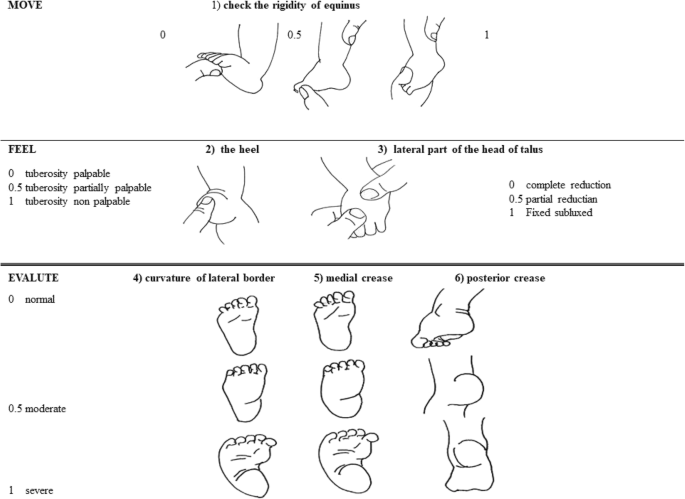



What A Paediatrician Should Know About Congenital Clubfoot Italian Journal Of Pediatrics Full Text




Club Foot Treatment Orthopaedic Institute For Children
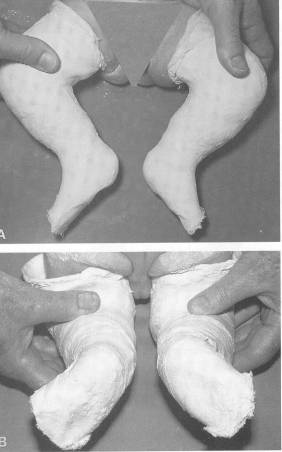



Clubfoot Congenital Equinovarus Cev Team Bone



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os




On World Clubfoot Day An Expert Answers All Your Questions About The Birth Deformity Parenting News The Indian Express



2
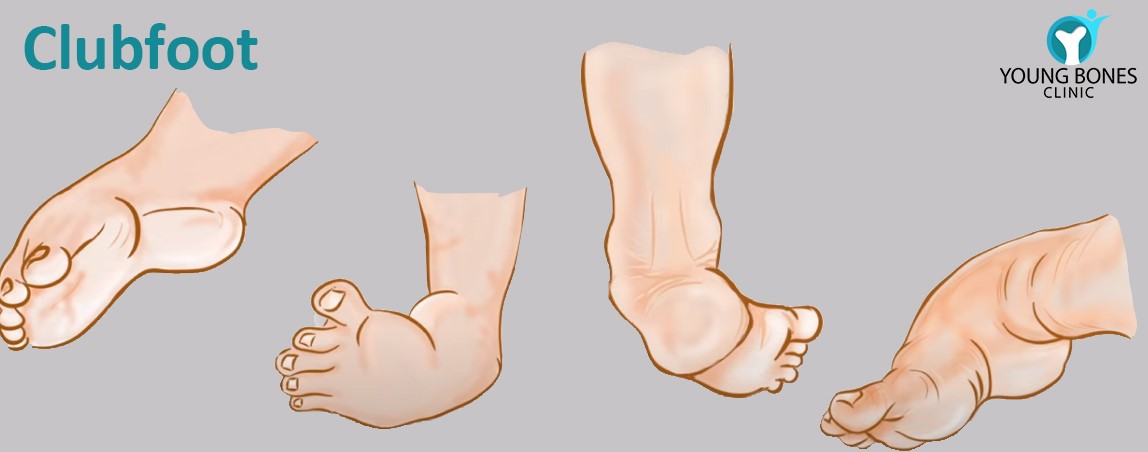



Clubfoot Treatment In Gurgaon Delhi Young Bones Clinic
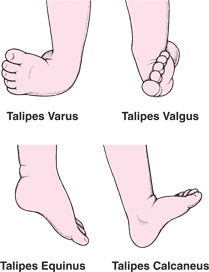



Congenital Talipus Equino Varus Physiotherapy Treatment In Ahmedabad




Congenital Idiopathic Clubfoot Prevention Of Late Deformity And Disability By Conservative Treatment With The Ponseti Technique Pediatric Annals




Clubfoot And Its Treatment Dr Michael Vohrer
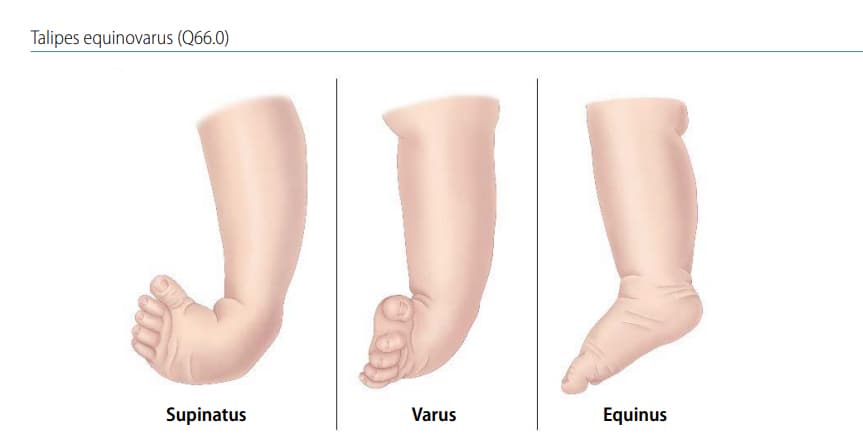



Chapter 4 9 Talipes Equinovarus Talipes Equinovarus Q66 0 Cdc
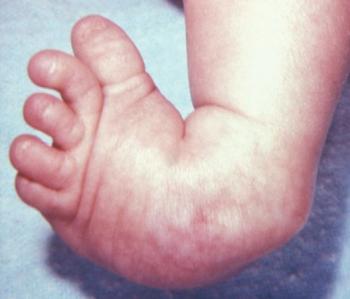



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments



1
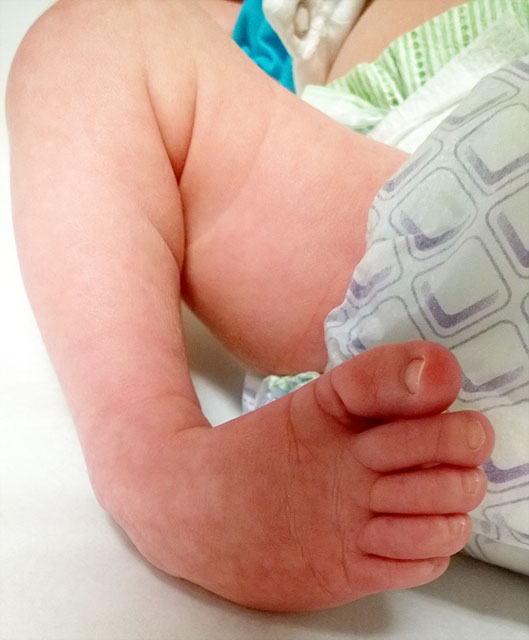



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine



Clubfoot What Is Clubfoot What Causes Clubfoot Who Gets Clubfoot What Are The Symptoms Of Clubfoot




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Congenital Clubfoot Prof Mohamed M



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿